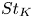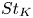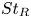97 results
Establishing a National Emergency Medical Team (EMT) in the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM)
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 37 / Issue S2 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2022, p. s107
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Particle subgrid stress models for large Stokes numbers in particle-laden turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of pharyngeal swallowing pressure using high-resolution manometry during transoral surgery for oropharyngeal cancer
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 135 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2021, pp. 153-158
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fluid Permeation Through A Membrane With Infinitesimal Permeability Under Reynolds Lubrication
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Mechanics / Volume 36 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 637-648
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Epidemiology of hospitalised paediatric community-acquired pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia following the introduction of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in the national immunisation programme in Japan
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, e91
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dust evolution in galaxies at z > 7
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S341 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 312-313
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A new galaxy Spectral Energy Distribution model with the evolution of dust consistent with chemical evolution
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S341 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 152-156
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Detections of far-infrared [OIII] and dust emission in a galaxy at z = 8.312: Early metal enrichment in the heart of the reionization era
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S341 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 211-215
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Efficacy of fluoroscopy-guided endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 132 / Issue 12 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2019, pp. 1128-1133
- Print publication:
- December 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detection of modified measles and super-spreader using a real-time reverse transcription PCR in the largest measles outbreak, Yamagata, Japan, 2017 in its elimination era
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 146 / Issue 13 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2018, pp. 1707-1713
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Voltage Contrast Imaging with Energy-Controlled Signal in an FE-SEM.
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2018, pp. 662-663
- Print publication:
- August 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Onset of calving at supraglacial lakes on debris-covered glaciers of the Nepal Himalaya
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 55 / Issue 193 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2017, pp. 909-917
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cold-Atom Ion Sources for Focused Ion Beam Applications
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 23 / Issue S1 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2017, pp. 276-277
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
24 - Cultural Diversity and Mental Health Treatment
- from Part III - Mental Health Systems and Policy: Introduction to Part III
-
-
- Book:
- A Handbook for the Study of Mental Health
- Published online:
- 28 May 2018
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2017, pp 493-511
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Numerical Simulation of Snowdrift Development
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 13 / 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 265-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
RACE AND ENVIRONMENTAL EQUITY
-
- Journal:
- Du Bois Review: Social Science Research on Race / Volume 13 / Issue 2 / Fall 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2016, pp. 215-219
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Occurrence of human respiratory syncytial virus in summer in Japan
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 145 / Issue 2 / January 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2016, pp. 272-284
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Correlative Characterization of Graphene with the Linkage of SEM and KFM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 22 / Issue S3 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2016, pp. 226-227
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Fossil ceratioid anglerfishes (Teleostei: Lophiiformes) from the Miocene of the Los Angeles Basin, California
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 82 / Issue 5 / September 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2015, pp. 996-1008
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adenosquamous carcinoma of unknown primary origin: a case report and literature review
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 129 / Issue S2 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2015, pp. S91-S94
- Print publication:
- March 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation