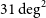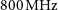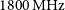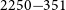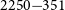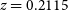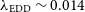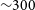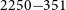69 results
Students’ emotional well-being and religiosity during the COVID-19 pandemic- an international study in 7 countries
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S406
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
TMS-EEG in the Investigation of Excitation-Inhibition Imbalance in Psychosis and Cognition
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, pp. S62-S63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
14 - Catholicism and Human Dignity in the Philippines
-
-
- Book:
- Human Dignity in Asia
- Published online:
- 26 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 15 September 2022, pp 332-355
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Role of saliva use during masturbation in the transmission of Chlamydia trachomatis in men who have sex with men
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2021, e216
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19 and its Cardiac and Neurological Complications among Ontario Visible Minorities
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2021, pp. 504-513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
EPA-0311 – The China Shenzhen Act Team: Development and Description of its Creation from the Experience of a Consultant
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue S1 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PKS 2250–351: A giant radio galaxy in Abell 3936
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2020, e013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
PS1 - 160 A Telephone Based Cognitive Assessment Tool for Brain Metastases Patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue S4 / October 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2016, p. S9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Geographical Dimension of Colonial Justice: Using GIS in Research on Law and History
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / November 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2016, pp. 1027-1045
- Print publication:
- November 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
F.04 Flow diversion in the treatment of aneurysms: A randomized care trial and registry
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue S2 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2016, p. S19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Emergence of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Nursing Homes With High Background Rates of MRSA Colonization
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 37 / Issue 8 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2016, pp. 983-986
- Print publication:
- August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Two-year follow-up of a Chinese sample at clinical high risk for psychosis: timeline of symptoms, help-seeking and conversion
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2016, pp. 287-298
-
- Article
- Export citation
The ASKAP/EMU Source Finding Data Challenge
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 32 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2015, e037
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Focused parathyroidectomy without intra-operative parathyroid hormone monitoring for primary hyperparathyroidism: results in a low-volume hospital
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 129 / Issue 8 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2015, pp. 788-794
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Duration of syphilis symptoms at presentations in men who have sex with men in Australia: are current public health campaigns effective?
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 144 / Issue 1 / January 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2015, pp. 113-122
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of Primitive Reflexes and Parkinsonian Signs in Dementia
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 5 / September 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2014, pp. 601-607
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation