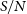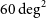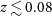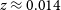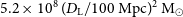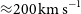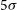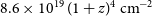427 results
D.1 Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of subcutaneous efgartigimod in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: results from the ADHERE trial
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. S8-S9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccines in the prevention of post-COVID conditions in children and adolescents: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modeling relaxed policies for discontinuation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus contact precautions
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing social cognition in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls using the reading the mind in the eyes test (RMET): a systematic review and meta-regression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 847-873
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Solvent-Kaolinite Interactions Investigated using the 3D-Rism-Kh Molecular Theory of Solvation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 286-296
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine in the prevention of post-COVID conditions: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of the latest research
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, e168
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
3 - Global Bird Communities of Alpine and Nival Habitats
-
-
- Book:
- Ecology and Conservation of Mountain Birds
- Published online:
- 30 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 July 2023, pp 90-136
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Benzodiazepine Prescription for Anxiety Disorders Increase the Risk of Substance Use Disorders: A Retrospective Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S324
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Effects of undergraduates’ chronotypes and perceived stress on their sleep quality: A cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S720
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The undergraduate nursing students’ encountering experience with recovery patients as educators
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S848
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and PTSD symptoms before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2022, pp. 5428-5441
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 43 - Geriatric Otolaryngology
- from Section III - Care of the Elderly by Organ System
-
-
- Book:
- Reichel's Care of the Elderly
- Published online:
- 30 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 July 2022, pp 536-547
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Phosphorylation of cysteine string protein-α up-regulates the frequency of cholinergic waves via starburst amacrine cells
-
- Journal:
- Visual Neuroscience / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2022, E003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Polygenic risk, familial liability and stress reactivity in psychosis: an experience sampling study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 7 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 2798-2807
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in children’s attachment security to mother and father after the birth of a sibling: Risk and resilience in the family
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2021, pp. 1404-1420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms in the adolescent offspring of mothers with anxiety and depressive symptoms. Findings from the raine study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. S88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The risk of anxiety symptoms in young adult offspring of parents with mental health problems: Findings from the raine study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S617-S618
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Longitudinal associations between alcohol use, smoking, genetic risk scoring and symptoms of depression in the general population: a prospective 6-year cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2021, pp. 1409-1417
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation