104 results
Ideality of Clay Membranes in Osmotic Processes: A Review
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 214-223
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Formation of Hydrotalcite-like Compounds During R7T7 Nuclear Waste Glass and Basaltic Glass Alteration
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 526-533
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An Fe-Berthierine from a Cretaceous Laterite: Part II. Estimation of Eh, pH and pCO2 Conditions of Formation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / August 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 580-586
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An Fe-Berthierine From A Cretaceous Laterite: Part I. Characterization
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / August 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 564-579
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Association of European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology practical recommendations for surveillance and prevention of cardiac disease in childhood cancer survivors: the importance of physical activity and lifestyle changes From the Association of European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology Working Group Sports Cardiology, Physical Activity and Prevention, Working Group Adult Congenital Heart Disease, Working Group Imaging and Working Group Heart Failure
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 250-261
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
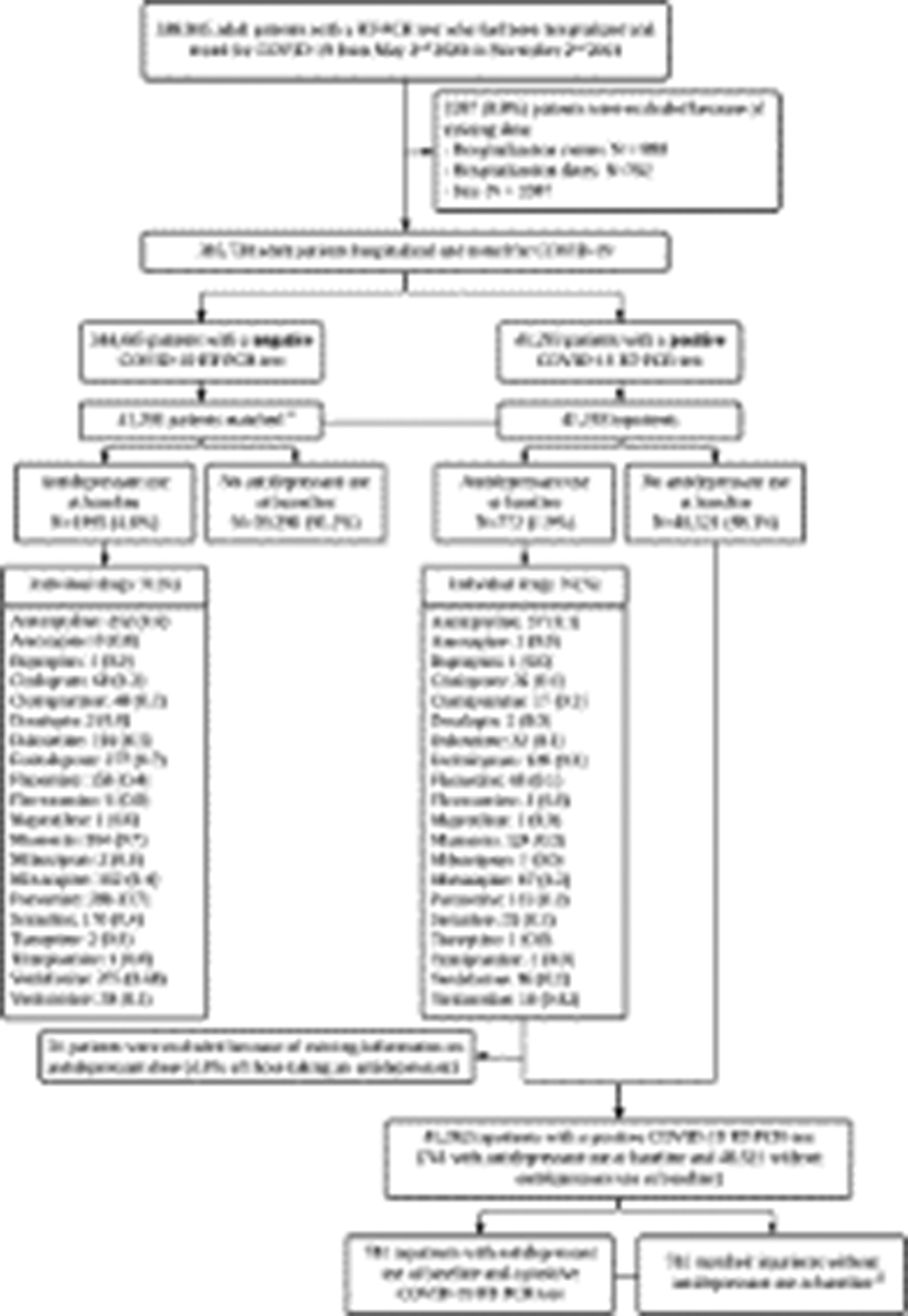
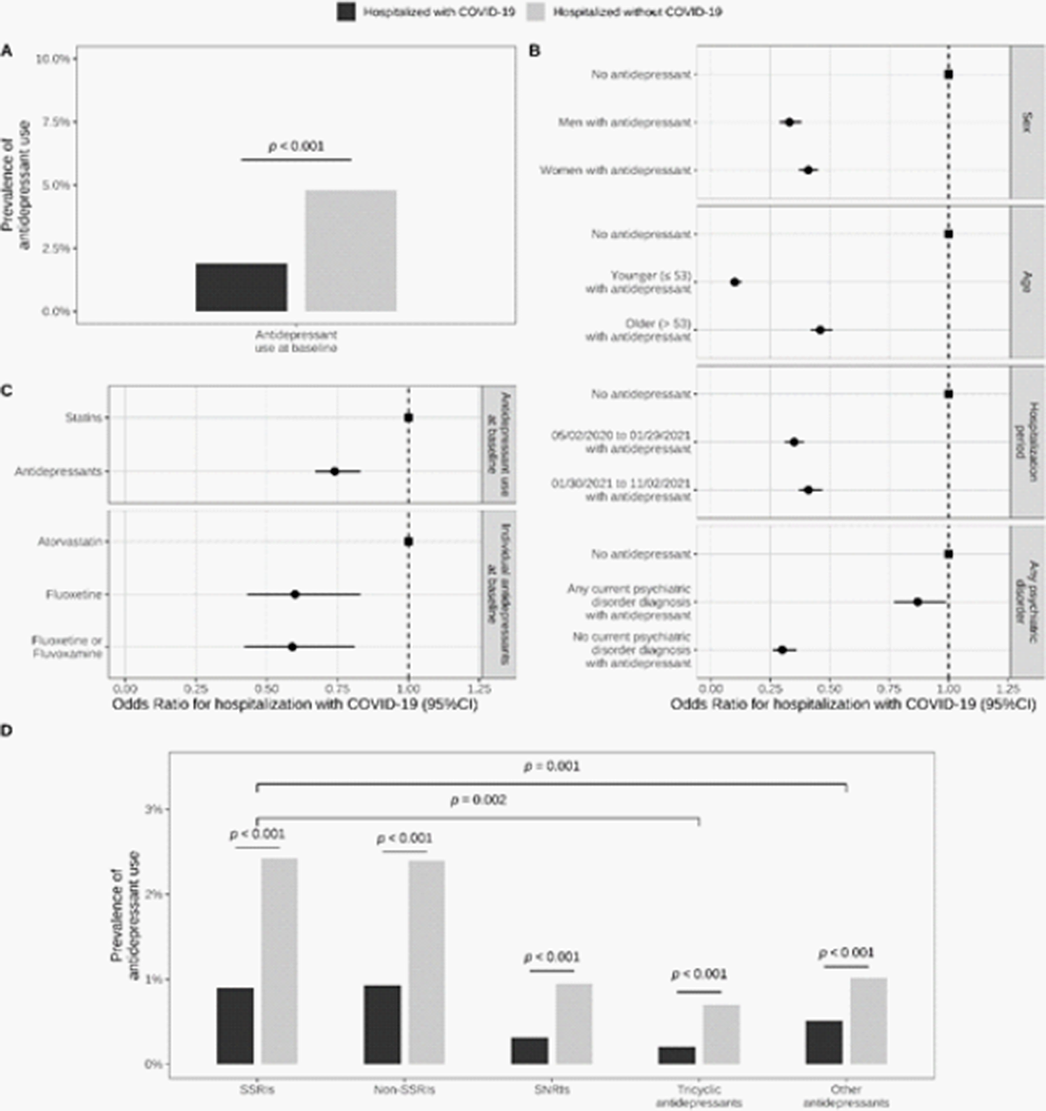
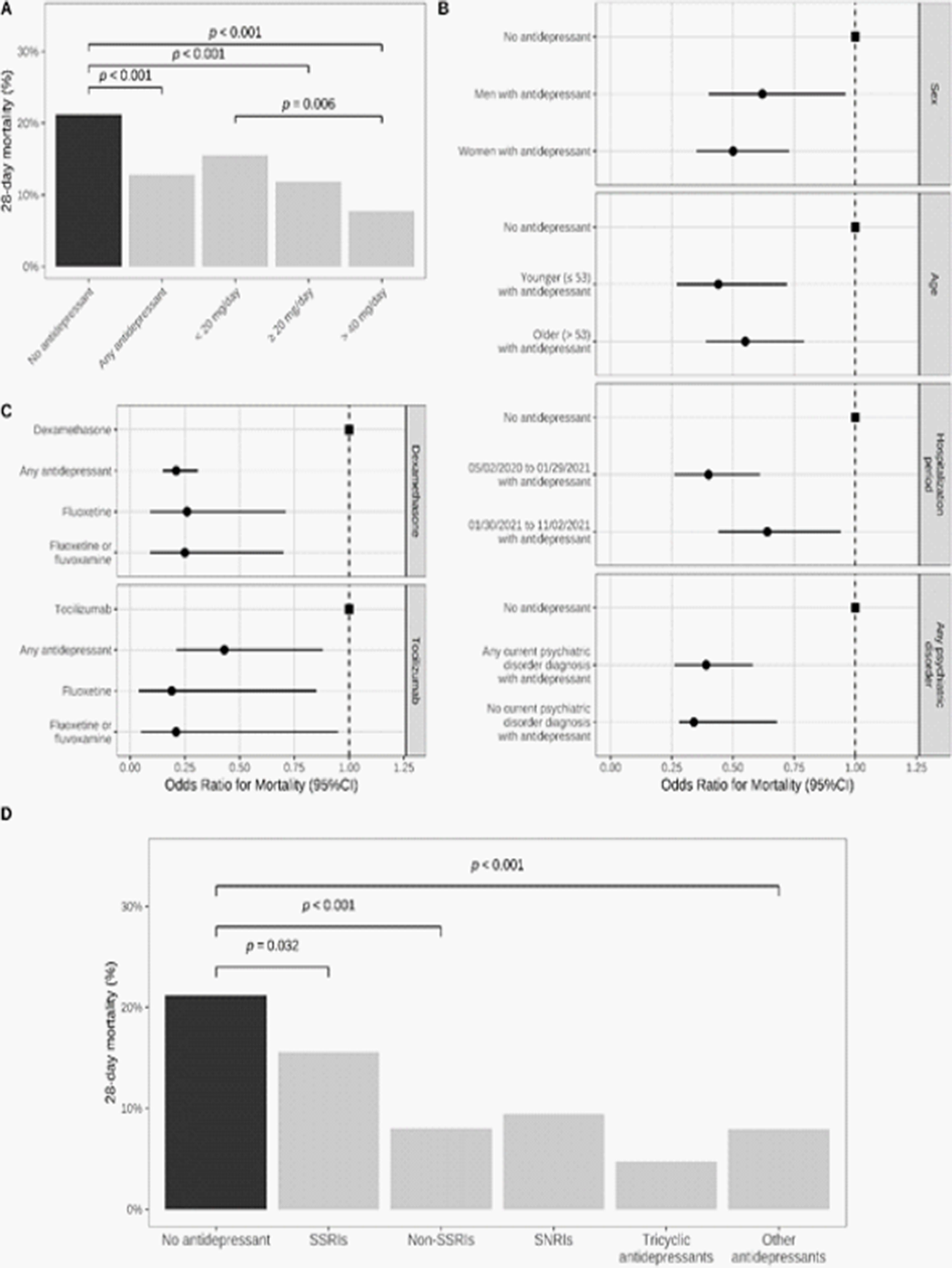
Antidepressant Use and Its Association with 28-Day Mortality in Inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: Support for the FIASMA Model against COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S118-S119
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Healthcare worker perceptions surrounding Staphylococcus aureus transmission and prevention practices in the neonatal intensive care unit
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, pp. 1953-1958
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deterring Digital Trade Without Discrimination
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- AJIL Unbound / Volume 117 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2023, pp. 104-109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Predicting extinctions with species distribution models
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Extinction / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pre-Feeding Agonism and Seasonality in Captive Groups of Chimpanzees (Pan Troglodytes)
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 2 / Issue 2 / May 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 153-163
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The northern bald ibis Geronticus eremita: history, current status and future perspectives
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Psychiatric beds and prison populations in 17 Latin American countries between 1991 and 2017: rates, trends and an inverse relationship between the two indicators
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 5 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2020, pp. 936-945
-
- Article
- Export citation
What is diatomite?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 96 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2020, pp. 48-52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neuroimaging Findings in Patients with Postpartum Psychoses
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 11 / Issue S4 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 259s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Acceptability on computerlzed self assessment in psychiatric inpatients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 13 / Issue S4 / 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 322s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Placebo response in antidepressant drug trials
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, pp. 115-118
-
- Article
- Export citation
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (RTMS) in major depression — Short-term antidepressive effects
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 13 / Issue S4 / 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 272s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P0262 - Measuring computer attitude in psychiatric inpatients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 23 / Issue S2 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. S377
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Self-awareness in chronic schizophrenia: Bilateral assessment of negative symptoms (BAINSA)
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 13 / Issue S4 / 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 292s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Particle drift potential of glyphosate plus 2,4-D choline pre-mixture formulation in a low-speed wind tunnel
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2020, pp. 520-527
-
- Article
- Export citation