329 results
Association of Early Tracheostomy with Length of Stay and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
391 Value estimation of the Diabetes Prevention Program: How well does clinical trial-based cost-effectiveness apply to the real world?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 116
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Emotions and behaviours of child and adolescent psychiatric patients during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, e47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring symptom clusters in mild cognitive impairment and dementia with the NIH Toolbox
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
61 Network Segregation Predicts Processing Speed in the Cognitively Healthy Oldest-old
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 367-368
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Impact of intensified prevention measures on the rate of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections among mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, e235
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strategies used for the COVID-OUT decentralized trial of outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Integrated safety analysis of phase 3 studies for investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent CDI
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s44-s45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Contribution of active surveillance cultures to the control of hospital-acquired carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an endemic hospital setting
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, pp. 188-195
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding Shield Laws
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / Fall 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, pp. 584-591
- Print publication:
- Fall 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cardiac magnetic resonance predictors for successful primary biventricular repair of unbalanced complete common atrioventricular canal
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, pp. 387-394
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 20 - Anesthesia for Endocrine Diseases
-
-
- Book:
- Cambridge Handbook of Anesthesiology
- Published online:
- 24 May 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 314-337
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
68 Metformin prevents the diagnosis of Long Covid in phase 3 trial of early treatment.
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 18-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Processing of social and monetary rewards in autism spectrum disorders
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, pp. 100-111
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validity of the NIH toolbox cognitive battery in a healthy oldest-old 85+ sample
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 6 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2022, pp. 605-614
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Efficacy and moderators of cognitive therapy versus behavioural activation for adults with depression: study protocol of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, e154
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
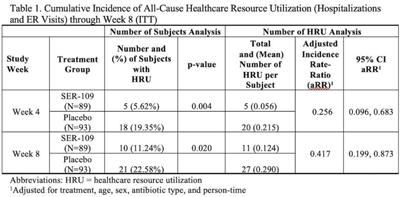
Healthcare resource utilization in a phase 3 trial of SER-109 in patients with recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, p. s73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Autism and autistic traits in those who died by suicide in England
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 221 / Issue 5 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2022, pp. 683-691
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk factors for Veteran food insecurity: findings from a National US Department of Veterans Affairs Food Insecurity Screener
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2021, pp. 819-828
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation