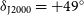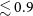198 results
L-Shell X-Ray Conversion Yields for Laser-Irradiated Tin and Silver Foils
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pathways to the medieval hospital: collective osteobiographies of poverty and charity
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empire and the Theology of Nature in the Cambridge Botanic Garden, 1760–1825
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2023, pp. 1011-1042
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jordan Goodman. Planting the World: Joseph Banks and His Collectors: An Adventurous History of Botany. London: William Collins, 2020. Pp. 560. $32.99 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 238-240
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Debiasing egocentrism and optimism biases in repeated competitions
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 7 / Issue 6 / November 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 761-767
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Archaeology and Social Justice in Native America – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2022, p. 864
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Archaeology and Social Justice in Native America
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2022, pp. 659-682
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Addressing the challenges of conducting community-engaged research during COVID-19: Rapid development and evaluation of a COVID-19 Research Patient and Community Advisory Board (PCAB)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2022, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The nascent coffee ring with arbitrary droplet contact set: an asymptotic analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 940 / 10 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2022, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
The third wind of language learning strategies research
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 55 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, pp. 417-421
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Do diets with higher carbon footprints increase the risk of mortality? A population-based simulation study using self-selected diets from the USA
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 2322-2328
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A randomised controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy for improving quality of life in people with muscle diseases
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 8 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2022, pp. 3511-3524
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of Escherichia coli resistance to fluoroquinolones in men undergoing prostate procedures: Is it time to change preoperative prophylaxis?
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2021, pp. 1078-1080
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The nascent coffee ring: how solute diffusion counters advection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 920 / 10 August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2021, A54
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 16 - The Cal-DSH Diversion Guidelines
- from Part II - Solutions
-
-
- Book:
- Decriminalizing Mental Illness
- Published online:
- 19 October 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 155-173
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Cal-DSH diversion guidelines
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 701-713
-
- Article
- Export citation
14 - The Physical and Social Environments as Determinants of Health: Implications for Substance and Behavioral Addictions
- from Part III - Levels of Analysis and Etiology
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Substance and Behavioral Addictions
- Published online:
- 13 July 2020
- Print publication:
- 06 August 2020, pp 182-198
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Impact of diet on CVD and diabetes mortality in Latin America and the Caribbean: a comparative risk assessment analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 9 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2020, pp. 2577-2591
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation