54 results
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-energy and high-peak-power GHz burst-mode all-fiber laser with a uniform envelope and tunable intra-burst pulses
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, e81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2.1
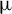 $\unicode{x3bc}$m, high-energy dissipative soliton resonance from a holmium-doped fiber laser system
$\unicode{x3bc}$m, high-energy dissipative soliton resonance from a holmium-doped fiber laser system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2023, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Record power and efficient mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in germania fiber with high stability
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Novel Pathway for Multi-scale High-resolution Time-resolved Residual Stress Evaluation of Laser-welded Eurofer97
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, p. 2126
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cancer mutation profiles predict ICIs efficacy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 24 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, e16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transmission pattern of shigellosis in Wuhan City, China: a modelling study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, e249
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tilting pairs in extriangulated categories
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2021, pp. 947-981
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations of genetic variants of miRNA coding regions with pulmonary tuberculosis risk in China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2021, e208
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of self-efficacy on first onset and prognosis of major depressive disorder: Findings from a longitudinal study in a sample of Chinese first-year university students – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2021, p. 199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of self-efficacy on first onset and prognosis of major depressive disorder: findings from a longitudinal study in a sample of Chinese first-year university students
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, pp. 178-183
-
- Article
- Export citation
Echinococcus shiquicus in Qinghai–Tibet plateau: population structure and confirmation of additional endemic areas
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 7 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2021, pp. 879-886
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations of genetic variants at TAP1 and TAP2 with pulmonary tuberculosis risk among the Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2021, e79
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Selective amplification of the chirped attosecond pulses produced from relativistic electron mirrors
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2020, pp. 287-292
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mid-infrared optical frequency comb in the 2.7–4.0 μm range via difference frequency generation from a compact laser system
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 8 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Retrospective analysis of clinical features in 134 coronavirus disease 2019 cases
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, e199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compliance with aspirin in paediatric CHD post-percutaneous transcatheter occlusion: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, pp. 1462-1468
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparative investigation of long-term oxidation behavior of selective laser melting–fabricated Inconel 718 at 650 °C
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2020, pp. 2036-2045
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the S-phase precipitates in 2024 aluminum alloy: An atomic-scale investigation using high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 12 / 29 June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 1582-1589
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation