12007 results
Channel Codes
- Classical and Modern
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- December 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 October 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Digitally mediated collaboration and participation: composing 10,427 miles and 11 hours apart
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Music Education , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Building Quantum Computers
- A Practical Introduction
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 11 July 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Why does perceived parenting in adolescence predict maladaptive personality in adulthood? Evidence for substantial genetic mediation
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Filtered handheld far-ultraviolet disinfection device in reducing environmental pathogens from high-touch clinical surfaces
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s97
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparison of Medicare Claims-based Clostridioides difficile infection classification to chart review using a linked cohort
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s61-s62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Two Novel Antibiotic Use Metrics for Facilities and Individual Prescribers in Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Settings
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s25-s26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
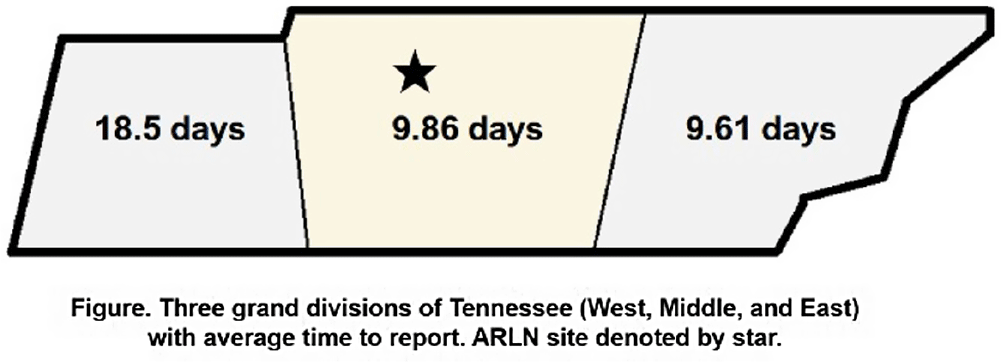
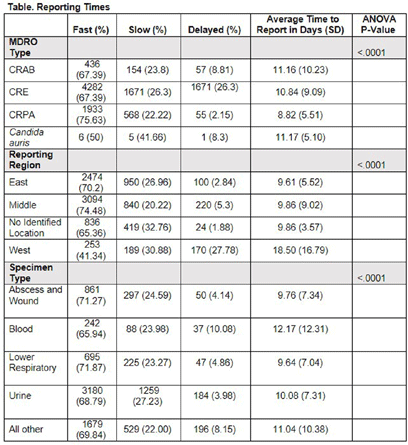
Variability of MDRO Reporting Across Tennessee Microbiology Laboratories
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
UTI Symptomatology and Antibiotic Prescribing among US Veterans Seen in Outpatient Clinics
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Antimicrobial Use in Veterans Affairs Community Living Centers, 2015 - 2019
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s6-s7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Budget Impact Analysis for the Spread and Financial Sustainability of Videoconference Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s45-s46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
High Prevalence of Laxative Use Among Those Tested for Clostridioides difficile Infection in VA Hospitals
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s78-s79
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
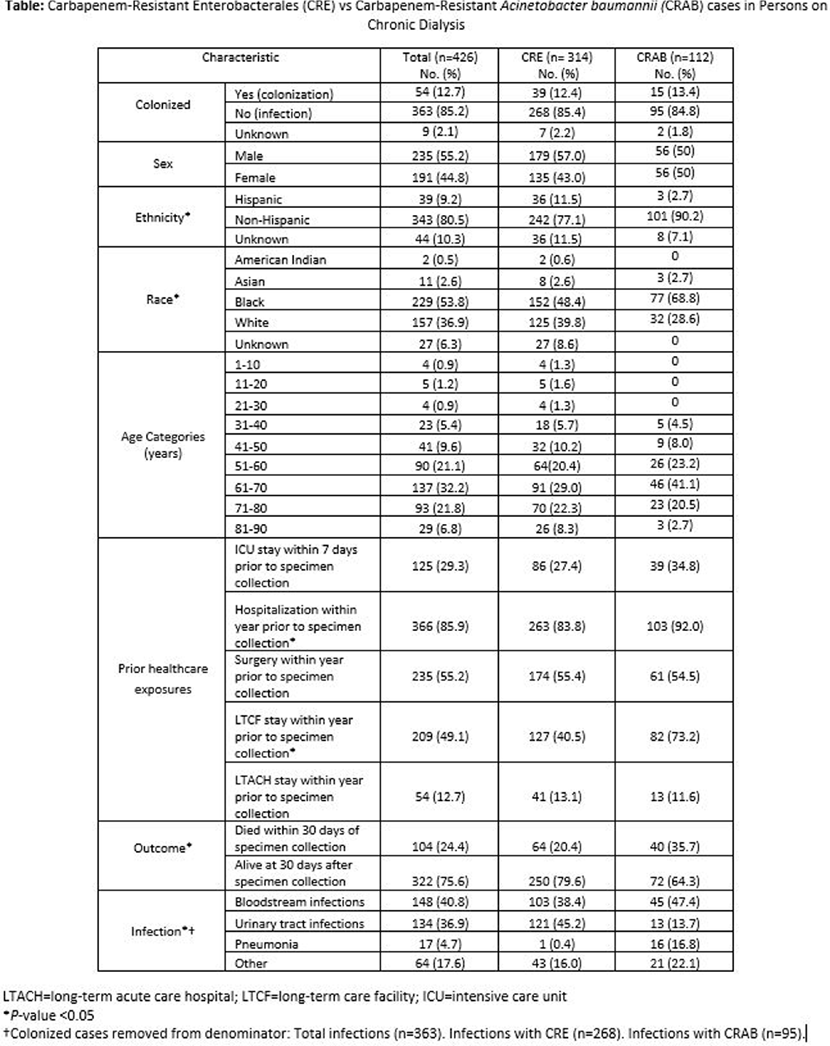
Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in US Dialysis Populations, 2016-2021
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s87-s88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Neoliberal Reason, Contemporary Music, and Proximal Critique
-
- Journal:
- Twentieth-Century Music , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
- Export citation
An automated faecal egg count system for detection of Ascaridia galli ova in chickens
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, e49
-
- Article
- Export citation
Health and Social Care Staff Awareness of Menopausal Symptoms in Adults With Intellectual Disability: Results From a Survey
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue S1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2024, p. S177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Quality Improvement Project on Standardising GP Discharge Summaries in Liaison Psychiatry Services for Older People in Nottinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue S1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2024, pp. S173-S174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Audit of Sub-Therapeutic Dosing of Methadone as Opioid Substitution Therapy
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue S1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2024, pp. S268-S269
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Safeguarding Asian tapir habitat in Sumatra, Indonesia
-
- Journal:
- Oryx , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Adsorption of Yeast RNA by Allophane
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / August 1979
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2024, pp. 261-268
-
- Article
- Export citation