In this article, self-focusing of an intense circularly polarized laser pulse in the presence of an external oblique magnetic field in hot magnetized plasma, using Maxwell’s equations and the relativistic fluid momentum equation, is studied. An envelope equation governing the spot size of the laser beam for both of left- and right-hand polarizations has been derived and the effects of the plasma temperature and oblique magnetic field on the electron density distribution of hot plasma with respect to variation of the normalized laser spot size has been investigated. Numerical results depict that in right-hand polarization, self-focusing of the laser pulse along the propagation direction in hot magnetized plasma becomes better and more compressed with increasing 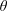 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$. Inversely, in left-hand polarization, increase of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$. Inversely, in left-hand polarization, increase of 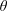 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ in an oblique magnetic field leads to enhancement of the spot size and reduction self-focusing. Besides, in the plasma density profile, self-focusing of the laser pulse improves in comparison with no oblique magnetic field. Also it is shown that plasma temperature has a key role in the laser spot size, normalized laser output power and the variation of plasma density.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ in an oblique magnetic field leads to enhancement of the spot size and reduction self-focusing. Besides, in the plasma density profile, self-focusing of the laser pulse improves in comparison with no oblique magnetic field. Also it is shown that plasma temperature has a key role in the laser spot size, normalized laser output power and the variation of plasma density.