No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
Considerable interest has been paid to laser-induced breakdown in liquid because of its wide application to medical issues of the eye and environmental monitoring. Therefore, the present work aims to study the phenomena of LIB in bulk distilled water generated in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) experiment. The effect of experimental parameters such as inter-pulse delay between the two lasers, laser pulse energy and detection time window have been studied to examine the temporal growth of the laser-induced plasma in bulk water. Electron density and plasma temperature have been determined. The Stark broadening profile has been utilized for the electron density determination where the hydrogen lines 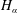 $H_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}}$ and
$H_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}}$ and 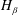 $H_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}}$ have been used. A deviation between electron density values from the broadening of both lines has been observed and discussed. The electron density values are varied between
$H_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}}$ have been used. A deviation between electron density values from the broadening of both lines has been observed and discussed. The electron density values are varied between 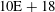 $10\text{E}+18$ and
$10\text{E}+18$ and 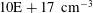 $10\text{E}+17~\text{cm}^{-3}$ corresponding to the timing experimental parameters. The plasma temperature is varied over a range 16 000
$10\text{E}+17~\text{cm}^{-3}$ corresponding to the timing experimental parameters. The plasma temperature is varied over a range 16 000 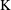 $\text{K}$ to 10 700
$\text{K}$ to 10 700 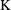 $\text{K}$ due to the plasma’s temporal behaviour with experimental parameters.
$\text{K}$ due to the plasma’s temporal behaviour with experimental parameters.