Article contents
Studies on the influence of structure units on the state of ytterbium ions in TeO2-based glasses
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 February 2020
Abstract
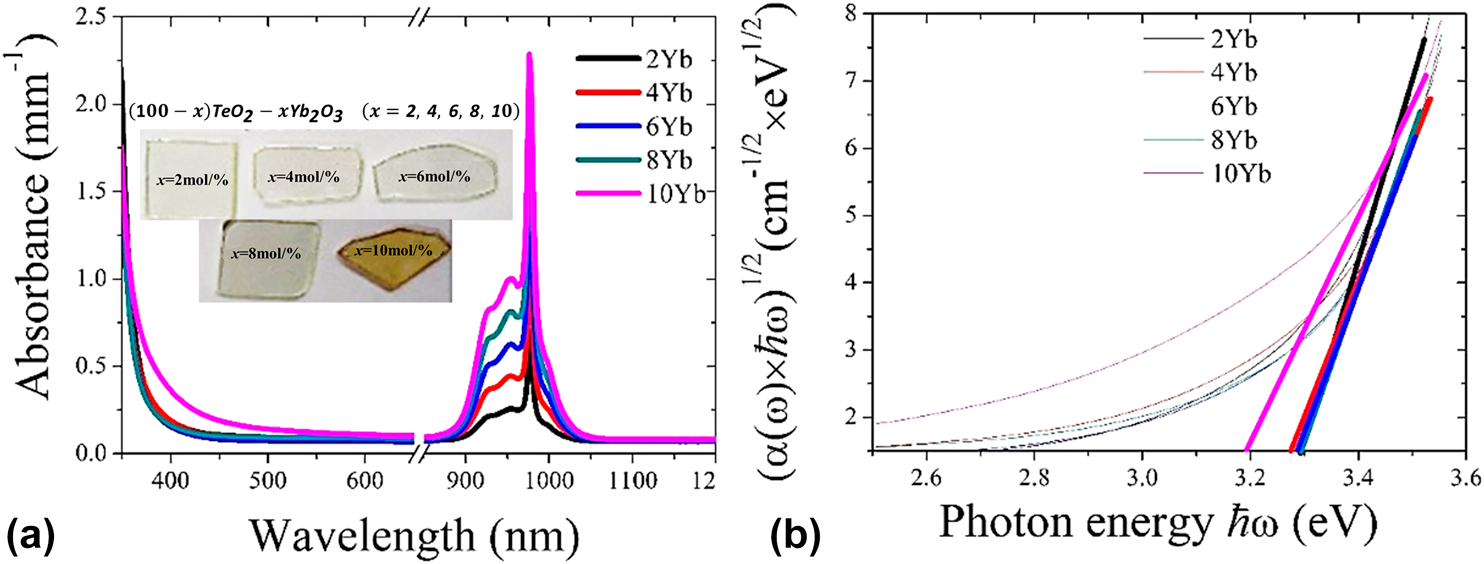
A simple composition of TeO2–Yb2O3 binary glass was selected as the host glass matrix for discussing the structure of tellurite glass with increasing Yb2O3 content. Raman spectra were measured to investigate the structure of the binary tellurite glasses, and upconversion and downconversion fluorescence characteristics were employed for discussing the relationship between the structural units and the state of Yb3+ in the tellurite glasses. The results suggested that the decrease of TeO4/2 in the glasses would result in the formation of Yb3+ clusters and Yb3+–O2− couple in the tellurite glasses, and then results in the decrease of cooperative upconversion and downconversion fluorescence intensity.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 1
- Cited by




