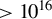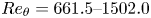664 results
TomoNet: A streamlined cryogenic electron tomography software pipeline with automatic particle picking on flexible lattices
-
- Journal:
- Biological Imaging / Volume 4 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A molecular perspective on the genera Paragonimus Braun, Euparagonimus Chen and Pagumogonimus Chen
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 73 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 295-299
-
- Article
- Export citation
Changes in the Properties of a Montmorillonite-Water System during the Adsorption and Desorption of Water: Hysteresis
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 38 / Issue 5 / October 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 485-492
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Effect of Clay Dispersion on the Sorption of Acetonitrile
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 355-358
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reactivity of Basal Surfaces, Steps and Edges of Muscovite: An AFM Study
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 3 / June 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 290-300
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validation of microRNAs regulated by vitamin D and lipid loading in immortalised hepatocytes
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E354
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ultrafast High-Energy Electron Radiography Application in Magnetic Field Delicate Structure Measurement
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Work hard and sleep better: Work autonomy attenuates the longitudinal effect of workaholism on sleep problem among Chinese working adults
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physics-constrained deep reinforcement learning for flow field denoising
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A CSR-based visible and infrared image fusion method in low illumination conditions for sense and avoid
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1321 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2023, pp. 489-503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-objective reward shaping for global and local trajectory planning of wing-in-ground crafts based on deep reinforcement learning
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1320 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2023, pp. 371-397
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distributed fixed-time control for six-degree-of-freedom spacecraft formation with event-triggered observer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1317 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 1968-1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Higher-order statistics and intermittency of a two-fluid Hall–Vinen–Bekharevich–Khalatnikov quantum turbulent flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 962 / 10 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Derivatives and Market (Il)liquidity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2023, pp. 157-194
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Oral and gastrointestinal bioaccessibility of anthocyanins in fresh, frozen, and blended blueberries
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, E10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depolarization of intense laser beams by dynamic plasma density gratings
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A transformer-based synthetic-inflow generator for spatially developing turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 957 / 25 February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A machine learning model for predicting the three-year survival status of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using multiple parameters
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 1041-1047
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation

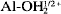 or Al-OH
or Al-OH