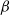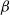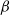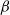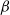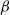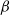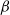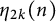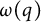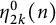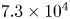1004 results
In-vacuum post-compression of optical probe pulse for relativistic plasma diagnostics
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
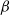 $\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
$\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Affinities between Asian non-human Schistosoma species, the S. indicum group, and the African human schistosomes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 76 / Issue 1 / March 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 7-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular phylogenetic position of Schistosoma sinensium in the genus Schistosoma
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 75 / Issue 3 / September 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 215-221
-
- Article
- Export citation
China’s prevention and control experience of echinococcosis: A 19-year retrospective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal Beam Dynamics for the Heavy-Ion Synchrotron Booster Ring at HIAF
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generation of energetic electrons by an electron cyclotron wave through stochastic heating in a spherical tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, 905890603
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotics for symmetrized positive moments of odd ranks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Disentangling the multigenerational transmissions of socioeconomic disadvantages and mental health problems by gender and across lineages: Findings from the Stockholm Birth Cohort Multigenerational Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S63-S64
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Internal shear layer and vortex shedding development of a structured porous coated cylinder using tomographic particle image velocimetry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 967 / 25 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2023, A17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation on the opposing jet penetration mode transition mechanism in the hypersonic flow
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1317 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2023, pp. 2047-2065
-
- Article
- Export citation
Co-developed implementation guidelines to maximize acceptability, feasibility, and usability of mobile phone supervision in Kenya
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cultural contributions to adults' self-rated mental health problems and strengths: 7 culture clusters, 28 societies, 16 906 adults
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 7581-7590
-
- Article
- Export citation
Programmable metamaterials
-
- Journal:
- Programmable Materials / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of backpressure on unstart and restart characteristics of a supersonic inlet
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1316 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 1774-1792
-
- Article
- Export citation
Post-operative vestibular and equilibrium evaluation in patients with cholesteatoma-induced labyrinthine fistulas
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 16-21
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Use of peripheral blood eosinophils to guide post-operative glucocorticoid therapy in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a randomised, controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2022, pp. 890-901
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Global trends and regional differences in the burden of anxiety disorders and major depressive disorder attributed to bullying victimisation in 204 countries and territories, 1999–2019: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2022, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prescribed-time cooperative guidance with time delay
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1311 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2022, pp. 852-875
-
- Article
- Export citation