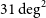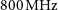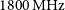146 results
Introduction to A Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections In Acute-Care Hospitals: 2022 Updates
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2023, pp. 1533-1539
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Executive Summary: A Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections in Acute-Care Hospitals: 2022 Updates
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 1540-1554
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of Ellescus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in North America: new species and synonyms revealed through integrative taxonomy – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 155 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Expert Consensus Statement: Anatomy, Imaging, and Nomenclature of Congenital Aortic Root Malformations
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, pp. 1060-1068
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
When not all three-dimensional anatomic teaching resources are the same
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2023, p. 1042
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of Ellescus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in North America: new species and synonyms revealed through integrative taxonomy
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 155 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2023, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tricuspid atresia and common arterial trunk: a rare form of CHD
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2022, pp. 1192-1195
-
- Article
- Export citation
A novel algorithm for classification of interatrial communications within the oval fossa in the newborn: Results from the Copenhagen Baby Heart Study
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1942-1949
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lodewyk H.S. van Mierop (March 31, 1927–October 17, 2021): a true giant
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2022, pp. 514-524
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The utility of a structured, interactive cardiac anatomy teaching session for resident education
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2022, pp. 208-212
-
- Article
- Export citation
Implementation of SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Infusion Sites at Three Medical Centers in the United States: Strengths and Challenges Assessment to Inform COVID-19 Pandemic and Future Public Health Emergency Use
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2022, e112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A left-sided veno-venous bridge
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2021, pp. 1007-1009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Whither heterotaxy?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1197-1199
-
- Article
- Export citation
All Change: an exploratory trial of lifestyle interventions in Scottish schoolchildren
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 67 / Issue OCE6 / May 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2021, E222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Eurasian strawberry blossom weevil, Anthonomus rubi (Herbst, 1795), is established in North America
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 579-585
-
- Article
- Export citation
Balloon dilatation versus surgical valvotomy for congenital aortic stenosis: a propensity score matched study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 12 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2021, pp. 1984-1990
-
- Article
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Publishing patterns and citation performance of manuscripts relating to paediatric cardiology and congenital heart disease: comparison of paediatric and adult cardiology journals
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 10 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2021, pp. 1608-1612
-
- Article
- Export citation