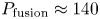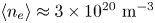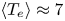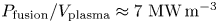159 results
Sperlingite, (H2O)K(Mn2+Fe3+)(Al2Ti)(PO4)4[O(OH)][(H2O)9(OH)]⋅4H2O, a new paulkerrite-group mineral, from the Hagendorf-Süd pegmatite, Oberpfalz, Bavaria, Germany.
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Optimization and control of synchrotron emission in ultraintense laser–solid interactions using machine learning – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dose-response relationships of seven dietary patterns with incident type 2 diabetes: Findings from the UK Biobank study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E313
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
11 - Collaboration
- from Part III - Collecting and Analysing Data
-
-
- Book:
- Conducting Research on Global Environmental Agreement-Making
- Published online:
- 07 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 10 August 2023, pp 210-227
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Versatile tape-drive target for high-repetition-rate laser-driven proton acceleration – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Automated control and optimization of laser-driven ion acceleration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Versatile tape-drive target for high-repetition-rate laser-driven proton acceleration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2023, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Natural area visitors’ potential role in preventing pathogen threats to amphibian biodiversity
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2023, pp. 142-147
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimization and control of synchrotron emission in ultraintense laser–solid interactions using machine learning
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Water masers high resolution measurements of the diverse conditions in evolved star winds
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 18 / Issue S380 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2024, pp. 389-391
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine intentions and uptake in a tertiary-care healthcare system: A longitudinal study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2021, pp. 1806-1812
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Serologic Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection over 6 Months of Follow Up in Healthcare Workers in Chicago: A Cohort Study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2021, pp. 1207-1215
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pathways to social inequality
-
- Journal:
- Evolutionary Human Sciences / Volume 3 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 July 2021, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Galeaclolusite, [Al6(AsO4)3(OH)9(H2O)4]⋅8H2O, a new bulachite-related mineral from Cap Garonne, France
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 85 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2020, pp. 142-148
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overview of the SPARC tokamak
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2020, 865860502
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Burden of respiratory syncytial virus hospitalisation among infants born at 32–35 weeks' gestational age in the Northern Hemisphere: pooled analysis of seven studies
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, e170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compositional principal component analysis generates gut microbiota profiles that associate with children's diet and body composition
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 79 / Issue OCE2 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, E284
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effectiveness of health checks to improve the physical health of people with severe mental illness in secondary care: A single blind cluster randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. S390-S391
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
10 - ‘Monstrous and Indefensible’? Newspaper Accounts of Sexual Assaults on Children in Nineteenth-Century England and Wales
- from Part III - Representation of Crime
-
-
- Book:
- Women's Criminality in Europe, 1600–1914
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 189-205
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 20 - Overview and Synthesis
-
-
- Book:
- Interactions in the Marine Benthos
- Published online:
- 07 September 2019
- Print publication:
- 29 August 2019, pp 488-505
-
- Chapter
- Export citation