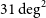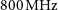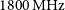47 results
P.020 Long-term safety and tolerability of atogepant 60mg once daily for preventive treatment of migraine: a phase 3, 40-week, multicenter extension to the advance trial
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey I: Design and first results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2020, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.057 Next-generation sequencing to determine a genetic cause of familial intracranial aneurysms
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 44 / Issue S2 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2017, p. S27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Clinical Gynecology
- Published online:
- 05 April 2015
- Print publication:
- 23 April 2015, pp viii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder: System Architecture and Specifications of the Boolardy Engineering Test Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 31 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2014, e041
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge History of World Music
- Published online:
- 05 December 2013
- Print publication:
- 12 December 2013, pp xv-xxiii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
GASKAP—The Galactic ASKAP Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 30 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2013, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Water Maser Emission Around Low/Intermediate Mass Evolved Stars
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 8 / Issue S287 / January 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2012, pp. 79-80
- Print publication:
- January 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Polarization properties of R Cas SiO masers
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 8 / Issue S287 / January 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2012, pp. 235-239
- Print publication:
- January 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Statistics and Galactic Properties of the Methanol Multibeam Survey
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 5 / Issue H15 / November 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2010, p. 800
- Print publication:
- November 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Star-formation masers in the Magellanic Clouds: A multibeam survey with new detections and maser abundance estimates
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 4 / Issue S256 / July 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2008, pp. 227-232
- Print publication:
- July 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Turbulent, steamy red supergiant winds
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 3 / Issue S242 / March 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2007, pp. 261-265
- Print publication:
- March 2007
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Methanol Multibeam Survey
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 3 / Issue S242 / March 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2007, pp. 218-222
- Print publication:
- March 2007
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Parkes methanol multibeam survey
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 2 / Issue S237 / August 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2006, p. 403
- Print publication:
- August 2006
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Personal Relationships
- Published online:
- 05 June 2012
- Print publication:
- 05 June 2006, pp xvii-xxii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A magnetically collimated jet from the evolved star W43A
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 2 / Issue S234 / April 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2006, pp. 267-270
- Print publication:
- April 2006
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Most Detailed Picture Yet of an Embedded High Mass YSO
-
- Journal:
- Symposium - International Astronomical Union / Volume 221 / 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2016, pp. 155-160
- Print publication:
- 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Detection of water vapor maser in a narrow-line Seyfert 1 nucleus
-
- Journal:
- European Astronomical Society Publications Series / Volume 10 / 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2003, p. 203
- Print publication:
- 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stellar masers: a review
-
- Journal:
- Symposium - International Astronomical Union / Volume 206 / 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2017, pp. 253-264
- Print publication:
- 2002
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation