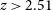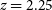521 results
The effectiveness of psychological treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials published over last 30 years
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
B.6 Long-term risk of subsequent stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GR.5 Establishing the utility of multi-platform liquid biopsy by integrating the CSF methylome and proteome in CNS malignancy
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Source Data Verification (SDV) quality in clinical research: A scoping review
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, e101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Host response of Nicotiana benthamiana to the parasitism of five populations of root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus coffeae, from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Facing the COVID-19 pandemic – an assessment of students’ mental health and major coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic – an international study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S152-S153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Characteristics of Adults Hospitalized for a Major Depressive Disorder: Results from the Multicenter OASIS-D Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S346-S347
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Measuring photometric redshifts for high-redshift radio source surveys
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Amisulpride Augmentation in Schizophrenia Patients with Poor Response to Olanzapine: A 4-week, Randomized, Rater-Blind, Controlled, Pilot Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1093
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
10 - Data Assimilation in the Near-Earth Electron Radiation Environment
- from Part II - ‘Fluid’ Earth Applications: From the Surface to the Space
-
-
- Book:
- Applications of Data Assimilation and Inverse Problems in the Earth Sciences
- Published online:
- 20 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 06 July 2023, pp 157-172
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A.5 Neurovascular complications of veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in critically ill COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.104 Grade 3 meningioma survival, recurrence and functional outcomes in an international multicenter cohort
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Post-operative vestibular and equilibrium evaluation in patients with cholesteatoma-induced labyrinthine fistulas
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 16-21
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Depolarization of intense laser beams by dynamic plasma density gratings
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mental health during pregnancy: The CONCEPTION study – Phase I
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S209-S210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surface area matters: An evaluation of swabs and surface area for environmental surface sampling of healthcare pathogens
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 5 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 834-836
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Opposition control of turbulent spots
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 943 / 25 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 June 2022, A3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Study on the monitoring and classification of winter wheat freezing injury in spring based on 3S technology
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 159 / Issue 9-10 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 623-635
-
- Article
- Export citation