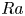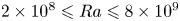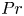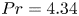254 results
High-elevation sheep and goat provisioning on the Tibetan Plateau, 3000–2200 BP
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long-term prehistoric human occupation in Western Tibet: excavations and surveys at the Xiada Co site
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The LCLS-II Photoinjector Laser Infrastructure
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Abnormal neural activation during negative emotion processing in anxiety disorders: a coordinate-based meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation

Forensic Linguistics in China
- Origins, Progress, and Prospects
-
- Published online:
- 04 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 02 May 2024
-
- Element
- Export citation
Experimental measurement of spatio-temporally resolved energy dissipation rate in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, A8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design of a Lens System Reduces Chromatic Aberration for Proton Radiography
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differentially Expressed microRNAs in Peritoneal Dialysis Effluent-Derived Exosomes from the Patients with Ultrafiltration Failure
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interlayer structure and dynamics of alkylammonium-intercalated smectites with and without water: A molecular dynamics study
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 55 / Issue 6 / December 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 554-564
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genotype-Phenotype Correlation Reanalysis in 83 Chinese Cases with OCRL Mutations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preventive effects of caffeine on nicotine plus high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and gain weight: a possible explanation for why obese smokers with high coffee consumption tend to be leaner
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1342-1351
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
EgCF mediates macrophage polarisation by influencing the glycolytic pathway
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, e101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Theoretical analysis of frequency modulation-to-amplitude modulation on the final optics and target of the SG II-Up laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hepatitis B antibody levels after different doses of hepatitis B vaccination: a retrospective study based on hospitalized children
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2023, e186
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The fragility index: how robust are the outcomes of head and neck cancer randomised, controlled trials?
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 451-456
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Common and distinct functional brain network abnormalities in adolescent, early-middle adult, and late adult major depressive disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 582-591
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rapid cold hardening and cold acclimation promote cold tolerance of oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) by physiological substances transformation and cryoprotectants accumulation
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2023, pp. 574-586
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between plasma and dietary trace elements and obesity in a rural Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, pp. 123-133
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Patterns of childhood maltreatment influence sleep quality: The role of emotion regulation
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2023, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation