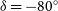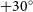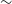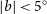267 results
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey V: Cataloguing the sky at 1 367.5 MHz and the second data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Establishing Disorder-Specific and Transdiagnostic Neural Features of Psychiatric Disorders Through Large-Scale Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Meta-Analyses
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S547-S548
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Neural Abnormalities Associated with Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Activation Studies
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S452
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Major Depressive Disorder Across Development and Course of Illness: A Functional Neuroimaging Meta-Analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S345-S346
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Major Depressive Disorder in Youth: A Meta-Analysis of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S219-S220
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Effects of Serotonergic Psychedelics on Neural Activity: A Meta-Analysis of Task-Based Functional Neuroimaging Studies
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S921
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Neural Basis of Major Depressive Disorder in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Activation Studies
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S158
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Influence of Lived Experiences on Public Responses to Future Diseases via (De)Sensitization of Concern
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2022, e251
-
- Article
- Export citation
Correlates of late-onset antipsychotic treatment resistance
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S781-S782
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Ethnic inequalities in treatment with clozapine
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S611
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Ethnic inequities in multimorbidity among people with psychosis: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, e52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey Paper II: First Stokes I Source Catalogue Data Release
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2021, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ASKAP Variables and Slow Transients (VAST) Pilot Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, e054
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relational Learning and Teaching with BME Students in Social Work Education
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2021, pp. 93-105
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Insights from electronic health record data to improve mental health service delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S38-S39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
8 - Memory in Hummingbirds
- from Part II - Memory and Recall
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Animal Cognition
- Published online:
- 01 July 2021
- Print publication:
- 22 July 2021, pp 174-189
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
‘Spending all this time stressing and worrying and calculating’: marginal food security and student life at a Diverse Urban University
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 10 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2021, pp. 2788-2797
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey I: Design and first results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2020, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation