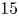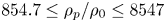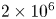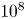110 results
Microplastics alter soil carbon cycling: Effects on carbon storage, CO2 and CH4 emission and microbial community
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Plastics / Volume 2 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tuning the Acidity of Montmorillonite by H3PO4-Activation and Supporting WO3 for Catalytic Dehydration of Glycerol to Acrolein
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 460-479
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Twin Pregnant Women With Anemia
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 4-5 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 313-318
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using nomogram scores to predict the early regression of coronary artery aneurysms of Kawasaki disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 348-355
-
- Article
- Export citation
Population dynamics and conservation status of the white-headed langur in the Chongzuo forest fragments, Guangxi, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the energy transport and heat transfer efficiency in radiatively heated particle-laden Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 953 / 25 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, A35
-
- Article
- Export citation
Understanding of turbulence modulation and particle response in a particle-laden jet from direct numerical simulations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 950 / 10 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2022, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Attitudes and Factors Associated With Intention to the Third Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Among Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Survey in 3 Provinces of China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2022, e201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RECENT PROGRESS IN ATMOSPHERIC FOSSIL FUEL CO2 TRENDS TRACED BY RADIOCARBON IN CHINA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2022, pp. 793-803
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influencing mechanisms of lifestyle and dietary factors on chronic diseases among community residents: updated evidence in Shanghai, China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2021, pp. 1233-1245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Soil organic carbon storage by shaded and unshaded coffee systems and its implications for climate change mitigation in China
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 158 / Issue 8-9 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2021, pp. 687-694
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Disease-Related Knowledge on Illness Perception and Psychological Status of Patients With COVID-19 in Hunan, China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2021, pp. 1415-1422
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A strategy for imaging-guided cocktail cancer therapy using dual-colored polymeric drug carriers with amplified aggregation-induced emission behavior by donor–acceptor/Förster resonance energy transfer adjustment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 23-24 / 14 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 3286-3295
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence of invasive aspergillosis in suspected pulmonary tuberculosis at a referral tuberculosis hospital in Shandong, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thrombocytopenia associated with transcatheter closure of giant patent ductus arteriosus
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 1896-1901
-
- Article
- Export citation