389 results
Structural and resting-state connection abnormalities of habenula in obsessive-compulsive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study on acoustic resonance of subsonic and slightly underexpanded impinging jets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Career Mobility and Performance Evaluation of China's SOE Managerial Elites
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Roles of MAPK and Nrf2 signaling pathways in quercetin alleviating redox imbalance induced by hydrogen peroxide in mammary epithelial cells
-
- Journal:
- Animal Nutriomics / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Workshop for the protection of Chinese giant salamanders
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The modulation of coherent structures by the near-wall motions of particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, A26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors governing the formation of lithiophorite at atmospheric pressure
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / June 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 353-360
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of Birnessite from the Oxidation of Mn2+ by O2 in Alkali Medium: Effects of Synthesis Conditions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 240-250
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Reaction Conditions on the Formation of Todorokite at Atmospheric Pressure
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / October 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 605-615
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Analysis Based on the Cancer Immunotherapy and Immune Activation of Gastric Cancer Patients
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship Between Pb2+ Adsorption and Average Mn Oxidation State in Synthetic Birnessites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 513-520
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bioinformatics-Based Identification of CircRNA-MicroRNA-mRNA Network for Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Mesoporous Magadiite Plates via Heterogeneous Nucleation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 61 / Issue 6 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 525-531
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural Controls on the Catalytic Polymerization of Hydroquinone by Birnessites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 525-537
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of Mn(III) availability on the phase transformation from layered buserite to tunnel-structured todorokite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / August 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 397-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Birnessites with Different Average Manganese Oxidation States Synthesized, Characterized, and Transformed to Todorokite at Atmospheric Pressure
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 6 / December 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 715-724
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction-Mediated Inhibition of Livin Expression Accelerates Ovarian Cancer Cell Apoptosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry and geological significance of the Tongjiang-Fuyuan Mesozoic magmatic rocks, NE China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1742-1760
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mismatch analysis of all-fiber coherent beam combiners based on the self-imaging effect
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation



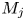
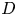
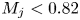
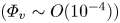
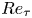
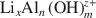 )-exchanged birnessite. The results show that the degree of conversion of lithiophorite decreases with decreasing reaction temperature. Lithiophorite can be obtained at pH values from 5.0 to 9.0, but a circumneutral pH is more favorable for formation at atmospheric pressure. Conversion of Na-birnessite (Bir-OH) to lithiophorite is more favored than aged Na-birnessite (Bir-OH-A). Lithiophorite was not obtained by refluxing the
)-exchanged birnessite. The results show that the degree of conversion of lithiophorite decreases with decreasing reaction temperature. Lithiophorite can be obtained at pH values from 5.0 to 9.0, but a circumneutral pH is more favorable for formation at atmospheric pressure. Conversion of Na-birnessite (Bir-OH) to lithiophorite is more favored than aged Na-birnessite (Bir-OH-A). Lithiophorite was not obtained by refluxing the 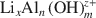 ion-exchanged H-birnessite (Bir-H) sample. The rate of conversion of lithiophorite increases with increasing reflux time. Lithiophorite synthesized by a reflux process has pseudo-hexagonal crystals of 0.1–0.5 µm with a chemical composition of Li
ion-exchanged H-birnessite (Bir-H) sample. The rate of conversion of lithiophorite increases with increasing reflux time. Lithiophorite synthesized by a reflux process has pseudo-hexagonal crystals of 0.1–0.5 µm with a chemical composition of Li