Article contents
DEGREE SPECTRA OF HOMEOMORPHISM TYPE OF COMPACT POLISH SPACES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 December 2023
Abstract
A Polish space is not always homeomorphic to a computably presented Polish space. In this article, we examine degrees of non-computability of presenting homeomorphic copies of compact Polish spaces. We show that there exists a 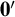 $\mathbf {0}'$-computable low
$\mathbf {0}'$-computable low $_3$ compact Polish space which is not homeomorphic to a computable one, and that, for any natural number
$_3$ compact Polish space which is not homeomorphic to a computable one, and that, for any natural number 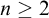 $n\geq 2$, there exists a Polish space
$n\geq 2$, there exists a Polish space 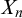 $X_n$ such that exactly the high
$X_n$ such that exactly the high $_{n}$-degrees are required to present the homeomorphism type of
$_{n}$-degrees are required to present the homeomorphism type of 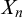 $X_n$. Along the way we investigate the computable aspects of Čech homology groups. We also show that no compact Polish space has a least presentation with respect to Turing reducibility.
$X_n$. Along the way we investigate the computable aspects of Čech homology groups. We also show that no compact Polish space has a least presentation with respect to Turing reducibility.
Keywords
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Association for Symbolic Logic
References
- 3
- Cited by





