Article contents
Zn2+–Eu3+ energy transfer and calculation of Eu3+5D0 quantum efficiency
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 September 2011
Abstract
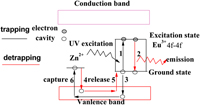
With 2 mol% Zn2+ codoping and 2 mol% K+ charge compensation, the red-emitting phosphor [K0.8Y0.63Eu3+0.08Zn0.02][Mo0.2W0.8O4] was synthesized by solid-state reaction. X-ray powder diffraction spectrum indicates that it owns single phase. Through its emission spectra, excitation spectra, and fluorescence decay curves measured, its emission mechanism was mentioned and it was calculated for its partial J-O parameters and quantum efficiency of Eu3+5D0 energy level under 395 nm excitation. The results indicate that Eu3+5D0 → 7F2 red luminescence in the host can be excited by 395 nm, but its quantum efficiency can be improved in space and it has potential applications for white light-emitting diode as the red luminescent materials.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by




