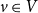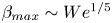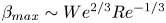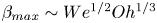134 results
Effectiveness of a WHO self-help psychological intervention to alleviate stress among healthcare workers in the context of COVID-19 in China: a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bosentan in the treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension in newborns: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Four-dimensional variational data assimilation of a turbulent jet for super-temporal-resolution reconstruction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Manipulating the Laser-Driven Proton Bunch with Plasma Wakefield
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plea Leniency and Prosecution Centredness in China's Criminal Process
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 254 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2023, pp. 448-465
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A simple European option pricing formula with a skew Brownian motion – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2023, p. 226
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A simple European option pricing formula with a skew Brownian motion
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2022, pp. 1029-1034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ensemble Kalman method for learning turbulence models from indirect observation data
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 949 / 25 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2022, A26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
VOLATILITY SWAPS VALUATION UNDER A MODIFIED RISK-NEUTRALIZED HESTON MODEL WITH A STOCHASTIC LONG-RUN VARIANCE LEVEL
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 250-263
-
- Article
- Export citation
In vivo study of a reserved atrial septal puncture area patent foramen ovale occluder
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2022, pp. 1581-1586
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Petrie cycle and Petrie tour partitions of 3- and 4-regular plane graphs
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2022, pp. 240-256
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Unexpected Alteration Colonic Mucus Appearance in the Constipation Model via an Intestinal Microenvironment
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1720-1733
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Scaling laws of the maximum spreading factor for impact of nanodroplets on solid surfaces
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 937 / 25 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2022, A12
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Judge as a Negotiator: Claims Negotiating and Inequalities in China’s Judicial Mediation
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 47 / Issue 4 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2021, pp. 1172-1200
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pre-hospital, in-hospital and post-hospital factors associated with sleep quality among COVID-19 survivors 6 months after hospital discharge: cross-sectional survey in five cities in China – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 6 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2021, e214
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pre-hospital, in-hospital and post-hospital factors associated with sleep quality among COVID-19 survivors 6 months after hospital discharge: cross-sectional survey in five cities in China
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 6 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, e191
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EDITORIAL: SPECIAL ISSUE ON FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS AND QUANTITATIVE FINANCE
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2021, pp. 101-103
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
AN ANALYTICAL APPROXIMATION FORMULA FOR THE PRICING OF CREDIT DEFAULT SWAPS WITH REGIME SWITCHING
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2021, pp. 143-162
-
- Article
- Export citation