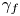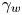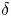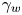41 results
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genesis of Palygorskite in the Neogene Baiyanghe Formation in Yangtaiwatan Basin, Northwest China, Based on the Mineralogical Characteristics and Occurrence of Enriched Trace Elements and Ree
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 23-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Genesis of Kaolinitic Claystone Deposits in the Datong Coalfield, Northern China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 68-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanosecond laser conditioning of multilayer dielectric gratings for picosecond–petawatt laser systems
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, e89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association study of urinary iodine concentrations and coronary artery disease among adults in the USA: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2018
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 12 / 28 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 2114-2122
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On two congruence conjectures of Z.-W. Sun involving Franel numbers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2023, pp. 887-905
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vertically neutral collapse of a pulsating bubble at the corner of a free surface and a rigid wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 962 / 10 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2023, A28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reduced cerebral cortex thickness is related to overexpression of exosomal miR-146a-5p in medication-free patients with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2022, pp. 6253-6260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multilayer dielectric grating pillar-removal damage induced by a picosecond laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2022, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prehistoric agricultural decision making in the western Himalayas: ecological and social variables
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rapid star identification algorithm for fish-eye camera based on PPP/INS assistance
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 75 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 928-945
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Six kilowatt record all-fiberized and narrow-linewidth fiber amplifier with near-diffraction-limited beam quality
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2 - How AI Can Help Depression Treatment
- from Part I - Personalized Medicine
-
-
- Book:
- Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare
- Published online:
- 21 April 2022
- Print publication:
- 05 May 2022, pp 15-36
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Palaeoclimate, palaeosalinity and redox conditions control palygorskite claystone formation: an example from the Yangtaiwatan Basin, northwest China
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 3 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2022, pp. 210-221
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adaptively robust filtering algorithm for maritime celestial navigation
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2021, pp. 200-212
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Poor vitamin D status and the risk of maternal depression: a dose–response meta-analysis of observational studies
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 8 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2020, pp. 2161-2170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ratios of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte predict all-cause mortality in inpatients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a retrospective cohort study in a single medical centre
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2020, e211
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MEMS-based dual temperature control measurement method for thermoelectric properties of individual nanowires
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, pp. 620-627
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation