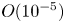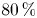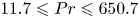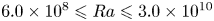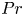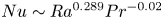116 results
SAMPLE PREPARATION SYSTEM FOR CARBONATE AND DIC IN WATER AT THE GXNU-AMS LABORATORY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
The melanin pigment gene black mediates body pigmentation and courtship behaviour in the German cockroach Blattella germanica
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 271-280
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-Temperature Transformation of Asbestos Tailings by Carbothermal Reduction
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 61 / Issue 1 / February 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 75-82
-
- Article
- Export citation
Direct Synthesis of 5A Zeolite From Palygorskite: The Influence of Crystallization Directing Agent on the Separation Performance for Hexane Isomers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE CHARGE-EXCHANGE CROSS-SECTIONS OF LOW-ENERGY CARBON IONS IN HELIUM AT GXNU
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Early stage of bubble spreading in a viscous ambient liquid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 964 / 10 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, A41
-
- Article
- Export citation
RADIOCARBON AND TRITIUM MEASUREMENTS AT THE GXNU-AMS FACILITY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic theory of Mack-mode receptivity in hypersonic boundary layers due to interaction of a heating/cooling source and a freestream sound wave
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2023, A34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular dynamics modelling of Na-montmorillonite subjected to uniaxial compression and unidirectional shearing
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 3-4 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2023, pp. 241-252
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparing mixed intertemporal tradeoffs with pure gains or pure losses
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 709-728
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NEW SAMPLE PREPARATION LINE FOR RADIOCARBON MEASUREMENTS AT THE GXNU LABORATORY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1501-1511
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
14C-AMS TECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO AN OIL FIELD TRACER EXPERIMENT
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2022, pp. 1159-1169
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Socioeconomic status, individual behaviors and risk for mental disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2022, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bounds on the mean and squared coefficient of variation of phase-type distributions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 880-889
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Petrogenesis of Triassic Caojian A-type rhyolites and associated I-type granites in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: rejuvenation of crystal mush
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, pp. 337-356
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of Prandtl number in quasi-two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 915 / 25 May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2021, A60
-
- Article
- Export citation
Differences and Correlation Analysis of Birth Weight and Overweight/Obesity in Shanghai Twin Cohort
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2021, pp. 29-36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neisseria meningitidis carriage and risk factors among teenagers in Suizhou city in China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2020, e227
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact dual-/tri-/quad-band bandpass filters with independently frequency-tunable and switchable passbands
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 13 / Issue 4 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2020, pp. 322-334
-
- Article
- Export citation