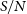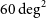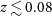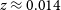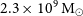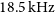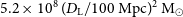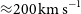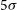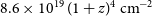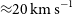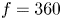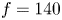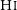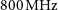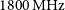188 results
Trends in incidence of self-harm, neurodevelopmental and mental health conditions among university students compared with the general population: nationwide electronic data linkage study in Wales
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Open or robotic? Radical cystectomies for patients with non-metastatic bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, e57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temporal trends of carbonated soft-drink consumption among adolescents aged 12–15 years from eighteen countries in Africa, Asia and the Americas
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2024, pp. 1633-1640
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
5.5 - Nociception and Pain
- from 5 - Neural Circuits
-
-
- Book:
- Cambridge Textbook of Neuroscience for Psychiatrists
- Published online:
- 08 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 171-176
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Epidemiology of central-line–associated bloodstream infection mortality in Canadian NICUs before and after 2017
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Subjective and objective sleep alterations in medication-naïve children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2023, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dose–response association of handgrip strength and risk of depression: a longitudinal study of 115 601 older adults from 24 countries
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 December 2022, pp. 135-142
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Instability evolution in the hypersonic boundary layer over a wavy wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 943 / 25 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 June 2022, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of data extraction errors in meta-analyses on the association between depression and peripheral inflammatory biomarkers: an umbrella review
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 5 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2021, pp. 2017-2030
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impaired Behavioral Pattern Separation in Refractory Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Mild Cognitive Impairment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2021, pp. 550-562
-
- Article
- Export citation
Food insecurity (hunger) and fast-food consumption among 180 164 adolescents aged 12–15 years from sixty-eight countries
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2021, pp. 470-477
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
30432 Novel insights from single-cell RNAseq analysis of the stromavascular fraction of human adipose tissue
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 5 / Issue s1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2021, pp. 4-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A metamorphosis of three-dimensional wave structure in transitional and turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 914 / 10 May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, A4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pediatric research priorities in healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial stewardship
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2020, pp. 519-522
- Print publication:
- May 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation