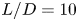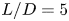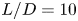214 results
Monitoring bird migration using nocturnal flight calls on the East Asian–Australasian Flyway: a case from Beijing
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 34 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contribution of diversity of social participation on the mental health of humanitarian migrants during resettlement
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A New Preparation Method for cis-1,4-polyisoprene/Na-montmorillonite Latex Composites by in situ Solution Emulsification
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 637-649
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation of millet grain size and cooking techniques across Asia between the late fourth and first millennia BC
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural Controls on the Catalytic Polymerization of Hydroquinone by Birnessites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 525-537
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of a Novel 15q21.1 Microdeletion in a Family with Marfan Syndrome
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conditional analysis on extreme wall shear stress and heat flux events in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Across Age-Groups
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 223-230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using nomogram scores to predict the early regression of coronary artery aneurysms of Kawasaki disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 348-355
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reduced-order variational mode decomposition to reveal transient and non-stationary dynamics in fluid flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 966 / 10 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Habitat selection and population status of breeding Wood Snipe Gallinago nemoricola in an alpine meadow in Sichuan, China
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, e54
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation and position-aiding performance analysis of Doppler observation from android smartphones
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 76 / Issue 2-3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 375-393
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Honey bee larval culture in vitro: gut emptying determines the transition from larva to prepupa and recombinant AccApidaecin improves antibacterial activity
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2023, pp. 368-379
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal analysis of mumps at township level in Wuhan, China, 2005–2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2023, e71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring the Genetic Association between Obesity and Serum Lipid Levels Using Bivariate Methods
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 25 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, pp. 234-244
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bubble re-acceleration behaviours in compressible Rayleigh–Taylor instability with isothermal stratification
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2023, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of caregiver-mediated intervention: a pilot study for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 23 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2022, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation