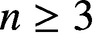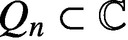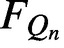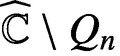50 results
Multidimensional Analysis of PANoptosis-Related Molecule CASP8: Prognostic Significance, Immune Microenvironment Effect, and Therapeutic Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Residents’ KABP and Social Support Statuses Under Normalized COVID-19 Pandemic Prevention and Control: A Cross-Sectional Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e79
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design and fabrication of optically transparent transmitarrays using inkjet-printing technology
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp v-vii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Abbreviations
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp xviii-xx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
14 - Adopting an Interdisciplinary Biosocial Approach to Determine the Conservation Implications of the Human–Gibbon Interface
-
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp 224-252
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Taxonomy, Ecology and Conservation of Cao Vit Gibbon (Nomascus nasutus) since Its Rediscovery
-
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp 6-23
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction
-
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp 1-5
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Foreword
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp xv-xvii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp viii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp 319-328
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Gibbon Conservation in the Anthropocene
-
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023
Asymptotic profiles for positive solutions of diffusive logistic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2023, pp. 273-284
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Advanced Crack Analytics on 3D X-ray Tomography of Irradiated Silicon Carbide Claddings
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 208-210
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Provenance and depositional history of the Mesozoic Sanjiang Basin (northeastern China): implications for the uplift history of the northeastern Asian continental margin
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 389-406
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ visualization of superior nanomechanical flexibility of individual ydroxyapatite nanobelts
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 1780-1781
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
STARLIKENESS AND CONVEXITY OF CAUCHY TRANSFORMS ON REGULAR POLYGONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 103 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2020, pp. 291-302
- Print publication:
- April 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acoustic feedback loops for screech tones of underexpanded free round jets at different modes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 902 / 10 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2020, A17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Development and validation of prognosis model of mortality risk in patients with COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2020, e168
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation