249 results
Testing maternal effects of vitamin-D and omega-3 levels on offspring neurodevelopmental traits in the Norwegian Mother, Father and Child Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depressive symptoms in adolescence and adult educational and employment outcomes: a structured life course analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A global pilot comparative, cross-sectional study of clinical research nurses/research midwives: Definition, knowledge base, and communication skills related to the conduct of decentralized clinical trials
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Head and Neck Cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines, Sixth Edition
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. S1-S224
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Systems-Thinking Model of Data Management and Use in US Archaeology
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Archaeological Practice / Volume 12 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2024, pp. 53-59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The predictive role of symptoms in COVID-19 diagnostic models: A longitudinal insight
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
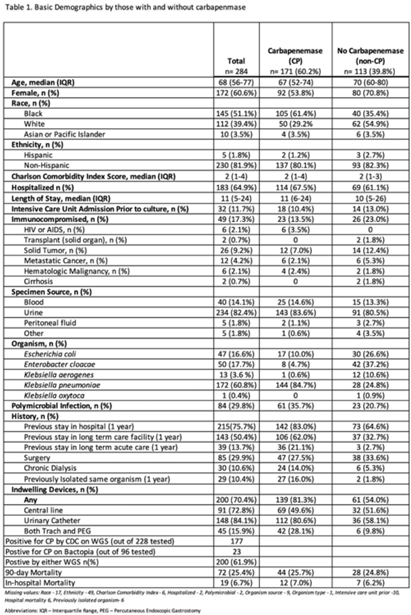
Evaluating indwelling devices and other risk factors for mortality in invasive Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales infections in Georgia, 2012–2019
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, e254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Increasing the equitability of data citation in paleontology: capacity building for the big data future
-
- Journal:
- Paleobiology / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2023, pp. 165-176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
98 On Combining In-Person and Remote National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) Uniform Data Set (UDS) data
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 500-501
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 Initial Application of Constraint-Induced Cognitive Therapy to Long COVID Brain Fog
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 598-599
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A new view of hillforts in the Andes: expanding coverage with systematic imagery survey
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Infant epigenetic aging moderates the link between Black maternal childhood trauma and offspring symptoms of psychopathology
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
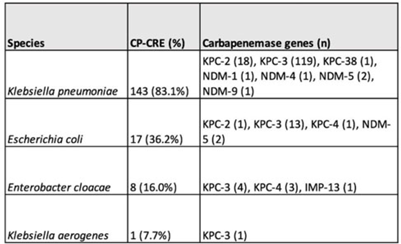
Carbapenemase genes and mortality in patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, Atlanta, Georgia, 2011–2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s12-s13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Investigation of the first cluster of Candida auris cases among pediatric patients in the United States―Nevada, May 2022
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s118-s119
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Pharmacogenetics of angiotensin modulators according to APOE-ϵ4 alleles and the ACE insertion/deletion polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 35 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 346-361
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recovery trajectories of IQ after pediatric TBI: A latent class growth modeling analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 August 2023, pp. 273-284
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strategies to build a positive and inclusive Antarctic field work environment
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 63 / Issue 87-89 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, pp. 125-131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stress and Coping Strategies Among Those Affected by Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Epidemic in Sierra Leone, West Africa
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, pp. s161-s162
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Family involvement, patient safety and suicide prevention in mental healthcare: ethnographic study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation