209 results
Subsurface scientific exploration of extraterrestrial environments (MINAR 5): analogue science, technology and education in the Boulby Mine, UK – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 23 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluating variation in pre-operative evaluation and planning for children undergoing atrial or ventricular septal defect repair
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 164-170
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alternative metrics for characterizing longer-term clinical outcomes in difficult-to-treat depression: I. Association with change in quality of life
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 6511-6523
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical research challenges posed by difficult-to-treat depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 419-432
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prehospital Ketamine Administration for Excited Delirium with Illicit Substance Co-Ingestion and Subsequent Intubation in the Emergency Department
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2021, pp. 697-701
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Herbicide diagnostics reveal multiple patterns of synthetic auxin resistance in kochia (Bassia scoparia)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 28-37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
55484 Dual activation of CAR and Nrf2 improves the efficacy: toxicity ratio of cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin-based treatment of TNBC
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 5 / Issue s1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2021, p. 98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Chapter 16 - The Cal-DSH Diversion Guidelines
- from Part II - Solutions
-
-
- Book:
- Decriminalizing Mental Illness
- Published online:
- 19 October 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 155-173
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 11 - Jail Diversion: A Practical Primer
- from Part II - Solutions
-
-
- Book:
- Decriminalizing Mental Illness
- Published online:
- 19 October 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 106-114
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Cal-DSH diversion guidelines
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 701-713
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in infants in a neonatal intensive care unit
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2020, pp. 1402-1408
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The contribution of orthographic input, phonological skills, and rise time discrimination to the learning of non-native phonemic contrasts
-
- Journal:
- Applied Psycholinguistics / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2020, pp. 481-516
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pediatric Practice Readiness for Disaster Response
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 15 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2020, pp. 277-281
-
- Article
- Export citation
Developing minimal-input techniques for invasive plant management: perimeter treatments enlarge native grass patches
-
- Journal:
- Invasive Plant Science and Management / Volume 13 / Issue 2 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2020, pp. 108-113
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jail diversion: a practical primer
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2020, pp. 651-658
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 16 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2019, p. 2816
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 8 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2019, pp. 1368-1380
-
- Article
- Export citation
Feasibility and acceptability of a Takeaway Masterclass aimed at encouraging healthier cooking practices and menu options in takeaway food outlets
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 22 / Issue 12 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2019, pp. 2268-2278
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection in pediatric inpatients: A meta-analysis and systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2019, pp. 420-426
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation

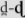 ], and [
], and [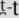 ]) by native English speakers. Moreover, because the [
]) by native English speakers. Moreover, because the [