Book contents
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 Infectious Conditions
- Section 2 Inflammatory Conditions
- Section 3 Hereditary and Genetic Conditions and Malformations
- Chapter 16 Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations
- Chapter 17 Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- Chapter 18 Cerebral Autosomal-Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)
- Chapter 19 Cerebral Autosomal-Recessive Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL)
- Chapter 20 Sickle Cell Disease and Other Hemoglobinopathies
- Chapter 21 Cerebrovascular Complications of Fabry Disease*
- Chapter 22 Marfan Syndrome
- Chapter 23 Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
- Chapter 24 Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
- Chapter 25 Progeria
- Chapter 26 MELAS Syndrome and Other Mitochondrial Disorders
- Chapter 27 Sturge–Weber Syndrome
- Chapter 28 Von Hippel–Lindau Disease
- Chapter 29 Familial Aneurysms
- Chapter 30 Cerebral Cavernous Malformations and Developmental Venous Anomalies
- Chapter 31 Cerebrovascular Manifestations of Neurofibromatosis
- Chapter 32 Menkes Disease
- Chapter 33 Wyburn–Mason Syndrome
- Chapter 34 Divry–van Bogaert Syndrome
- Chapter 35 Blue Rubber Bleb Syndrome
- Section 4 Vascular Conditions of the Eyes, Ears, and Brain
- Section 5 Disorders Involving Abnormal Coagulation
- Section 6 Systemic Disorders That Also Involve the Cerebrovascular System
- Section 7 Non-Inflammatory Disorders of the Arterial Wall
- Section 8 Venous Occlusive Conditions
- Section 9 Vasospastic Conditions and Other Miscellaneous Vasculopathies
- Index
- Plate Section (PDF Only)
- References
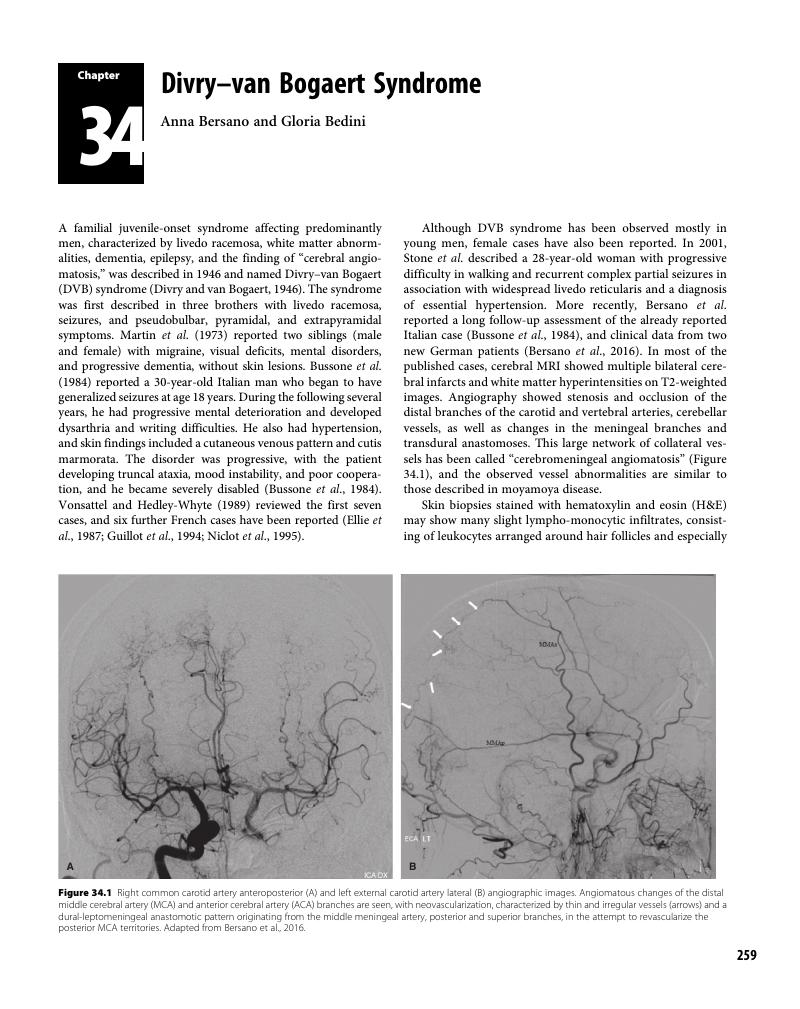
Chapter 34 - Divry–van Bogaert Syndrome
from Section 3 - Hereditary and Genetic Conditions and Malformations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 June 2018
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 Infectious Conditions
- Section 2 Inflammatory Conditions
- Section 3 Hereditary and Genetic Conditions and Malformations
- Chapter 16 Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations
- Chapter 17 Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- Chapter 18 Cerebral Autosomal-Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)
- Chapter 19 Cerebral Autosomal-Recessive Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL)
- Chapter 20 Sickle Cell Disease and Other Hemoglobinopathies
- Chapter 21 Cerebrovascular Complications of Fabry Disease*
- Chapter 22 Marfan Syndrome
- Chapter 23 Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
- Chapter 24 Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
- Chapter 25 Progeria
- Chapter 26 MELAS Syndrome and Other Mitochondrial Disorders
- Chapter 27 Sturge–Weber Syndrome
- Chapter 28 Von Hippel–Lindau Disease
- Chapter 29 Familial Aneurysms
- Chapter 30 Cerebral Cavernous Malformations and Developmental Venous Anomalies
- Chapter 31 Cerebrovascular Manifestations of Neurofibromatosis
- Chapter 32 Menkes Disease
- Chapter 33 Wyburn–Mason Syndrome
- Chapter 34 Divry–van Bogaert Syndrome
- Chapter 35 Blue Rubber Bleb Syndrome
- Section 4 Vascular Conditions of the Eyes, Ears, and Brain
- Section 5 Disorders Involving Abnormal Coagulation
- Section 6 Systemic Disorders That Also Involve the Cerebrovascular System
- Section 7 Non-Inflammatory Disorders of the Arterial Wall
- Section 8 Venous Occlusive Conditions
- Section 9 Vasospastic Conditions and Other Miscellaneous Vasculopathies
- Index
- Plate Section (PDF Only)
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke , pp. 259 - 267Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018

