Article contents
A study on surfactant-free growth of silver-carbon nanocables by H2SO4-mediated hydrothermal process
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 August 2011
Abstract
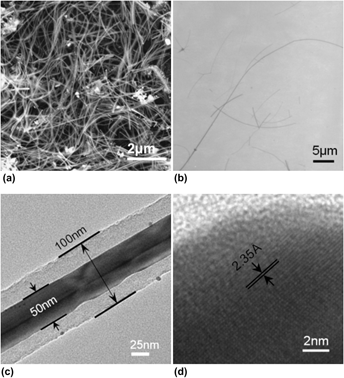
We study the one-pot facile hydrothermal growth of ultralong silver–carbon (Ag–C) nanocables with Ag nanowires as the cores and carbon as the sheaths through the mediation of H2SO4 and without using an organic surfactant. In the investigation, Ag–C nanostructures were systematically and extensively examined as a function of both temperature and H2SO4 concentration to locate the optimal conditions for preparing ultralong, robust, and uniform Ag–C coaxial nanocables at T = 180 °C and 0.5 M H2SO4. The characterization clearly demonstrated a simple, efficient, and surfactant-free synthesis of Ag–C nanocables. In the hydrothermal process, glycerol acts as both reducing agent and carbon source, while H2SO4 mediates the directional growth of the silver nanowire core and assists the deposition of carbon. Moreover, the nanocables manifest unusual ferromagnetism at room temperature and a plausible mechanism of forming Ag–C nanocables was proposed as a result of the chain-like hydrogen sulfate compounds owing to the H2SO4 mediation.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by




