Article contents
Electrochemical and kinetic study of as-cast and as-quench Mg2Ni-type hydrogen storage alloys
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 September 2013
Abstract
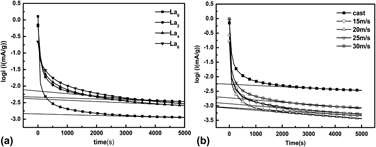
To improve the electrochemical and kinetic performances of the Mg2Ni-type hydrogen storage alloys, Mg was partially substituted by La, and the rapid solidification technology was used for the preparation of Mg20−xLaxNi10 (x = 0, 2, 4, 6) alloys. The microstructures of the as-cast Mg20−xLaxNi10 (x = 0, 2, 4, 6) and as-spun Mg20−xLaxNi10 (x = 2) alloys were systematically studied through x-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electronic microscopy. Electrochemical hydrogen storage properties were measured by the automatic galvanostatic system. Electrochemical impedance spectrum, linear polarization, and step-potential discharge curves were plotted using electrochemical workstation. The results showed that substitution of La for Mg was helpful for forming multiphase structures, increasing the discharge capacity of the as-cast Mg20−xLaxNi10 (x = 0, 2, 4, 6) alloys. The increasing quenching rate facilitated the formation of amorphous and nanocrystalline structures of Mg18La2Ni10 (La2) alloy, effectively improving the electrochemical and kinetic properties of Mg18La2Ni10 (La2) alloys.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by




