Article contents
Microstructures and hardness properties of laser clad Ni base two-phase intermetallic alloy coating
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 September 2017
Abstract
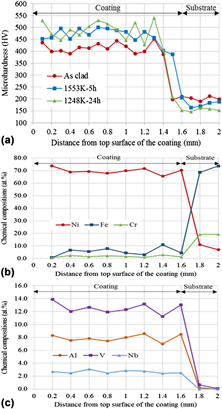
The two-phase Ni3Al and Ni3V intermetallic alloy laser clad on substrate of SUS304 was evaluated by hardness measurement, scanning electron microscopy, electron probe microanalyzer and transmission electron microscopy observations, focusing on the effect of post annealing after laser irradiation. The laser clad coating layer was diluted with approximately 5.4 at.% Fe and 1.6 at.% Cr stemming from the substrate. In the as-clad coating layer, the inhomogeneous eutectoid microstructure due to incomplete phase separation into two intermetallic phases Ni3Al and Ni3V took place. The hardness in the as-clad coating layer was lower than that in post annealed coating layers. In the coating layer annealed at 1553 K for 5 h, a dual two-phase microstructure composed of the primary cuboidal Ni3Al surrounded by the channel regions in which the major constituent is the Ni3V phase was observed, indicating that the complete eutectoid microstructure was developed. In the coating layer annealed at 1248 K for 24 h, the developed microstructure was lamellar-like one composed of the Ni3Al and Ni3V phases. The hardness in the coating layer annealed at 1248 K was the highest in the coatings observed in this study.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 32 , Issue 24: Focus Issue: Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Advanced Metallic Alloys—in Honor of Prof. Haël Mughrabi PART B , 28 December 2017 , pp. 4531 - 4540
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Mathias Göken
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by





