Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lester, Daniel R.
Dentz, Marco
Le Borgne, Tanguy
and
de Barros, Felipe P. J.
2018.
Fluid deformation in random steady three-dimensional flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 855,
Issue. ,
p.
770.
Boufadel, Michel
Geng, Xiaolong
An, Chunjiang
Owens, Edward
Chen, Zhi
Lee, Kenneth
Taylor, Elliott
and
Prince, Roger C.
2019.
A Review on the Factors Affecting the Deposition, Retention, and Biodegradation of Oil Stranded on Beaches and Guidelines for Designing Laboratory Experiments.
Current Pollution Reports,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 4,
p.
407.
Geng, Xiaolong
Boufadel, Michel C.
Lee, Kenneth
and
An, Chunjiang
2020.
Characterization of Pore Water Flow in 3‐D Heterogeneous Permeability Fields.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 3,
Geng, Xiaolong
Michael, Holly A.
Boufadel, Michel C.
Molz, Fred J.
Gerges, Firas
and
Lee, Kenneth
2020.
Heterogeneity Affects Intertidal Flow Topology in Coastal Beach Aquifers.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 17,
Icardi, Matteo
and
Dentz, Marco
2020.
Probability density function (PDF) models for particle transport in porous media.
GEM - International Journal on Geomathematics,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 1,
Geng, Xiaolong
Heiss, James W.
Michael, Holly A.
Boufadel, Michel C.
and
Lee, Kenneth
2020.
Groundwater Flow and Moisture Dynamics in the Swash Zone: Effects of Heterogeneous Hydraulic Conductivity and Capillarity.
Water Resources Research,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 11,
Soltanian, Mohamad Reza
Behzadi, Faranak
and
J. de Barros, Felipe P.
2020.
Dilution enhancement in hierarchical and multiscale heterogeneous sediments.
Journal of Hydrology,
Vol. 587,
Issue. ,
p.
125025.
Geng, Xiaolong
Boufadel, Michel C.
Rajaram, Harihar
Cui, Fangda
Lee, Kenneth
and
An, Chunjiang
2020.
Numerical Study of Solute Transport in Heterogeneous Beach Aquifers Subjected to Tides.
Water Resources Research,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 3,
Lester, Daniel R.
Dentz, Marco
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Le Borgne, Tanguy
2021.
The Lagrangian kinematics of three-dimensional Darcy flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 918,
Issue. ,
Yoon, Seonkyoo
Dentz, Marco
and
Kang, Peter K.
2021.
Optimal fluid stretching for mixing-limited reactions in rough channel flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 916,
Issue. ,
Wallace, Corey D.
Tonina, Daniele
McGarr, Jeffrey T.
de Barros, Felipe P. J.
and
Soltanian, Mohamad Reza
2021.
Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrous Oxide Emission Hotspots in Heterogeneous Riparian Sediments.
Water Resources Research,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 12,
Geng, Xiaolong
Heiss, James W.
Michael, Holly A.
Li, Hailong
Raubenheimer, Britt
and
Boufadel, Michel C.
2021.
Geochemical fluxes in sandy beach aquifers: Modulation due to major physical stressors, geologic heterogeneity, and nearshore morphology.
Earth-Science Reviews,
Vol. 221,
Issue. ,
p.
103800.
Lester, Daniel R.
Dentz, Marco
Bandopadhyay, Aditya
and
Le Borgne, Tanguy
2022.
Fluid deformation in isotropic Darcy flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 945,
Issue. ,
Ren, Wanli
Ershadnia, Reza
Wallace, Corey D.
LaBolle, Eric M.
Dai, Zhenxue
de Barros, Felipe P. J.
and
Soltanian, Mohamad R.
2022.
Evaluating the Effects of Multiscale Heterogeneous Sediments on Solute Mixing and Effective Dispersion.
Water Resources Research,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 9,
Ma, Ziqi
Dai, Zhenxue
Zhang, Xiaoying
Zhan, Chuanjun
Gong, Huili
Zhu, Lin
Wallace, Corey D.
and
Soltanian, Mohamad Reza
2022.
Dispersivity variations of solute transport in heterogeneous sediments: numerical and experimental study.
Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 2,
p.
661.
Li, Zijing
Zhang, Chunwei
Kaito, Kazuki
Hu, Yingxue
and
Suekane, Tetsuya
2022.
Experimental characterization of shear-enhanced dispersion in porous media.
Advances in Water Resources,
Vol. 170,
Issue. ,
p.
104325.
Dentz, Marco
Hidalgo, Juan J.
and
Lester, Daniel
2023.
Mixing in Porous Media: Concepts and Approaches Across Scales.
Transport in Porous Media,
Vol. 146,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
5.
Bonazzi, Alessandra
Jha, Birendra
and
de Barros, Felipe P.J.
2023.
Influence of initial plume shape on miscible porous media flows under density and viscosity contrasts.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 972,
Issue. ,
Geng, Xiaolong
Boufadel, Michel C.
Li, Hailong
Na Nagara, Viravid
and
Lee, Kenneth
2023.
Impacts of Evaporation‐Induced Groundwater Upwelling on Mixing Dynamics in Shallow Wetlands.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 15,
Zhang, Xueyi
Dou, Zhi
Chen, Zhou
Zhu, Wenyuan
Wang, Jinguo
and
Zhou, Zhifang
2023.
Uncovering asymmetrical mass transfer in layered porous media: Insights from pore-scale analysis.
Journal of Hydrology,
Vol. 623,
Issue. ,
p.
129790.
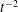 $t^{-2}$. For heterogeneous porous media, the mixing of the solute blob is determined by the random sampling of flow and deformation heterogeneity along trajectories, a mechanism different from persistent shear. We derive explicit perturbation theory expressions for stretching-enhanced solute mixing that relate the medium structure and mixing behaviour. The solution is valid for moderate heterogeneity. The random sampling of shear along trajectories leads to a
$t^{-2}$. For heterogeneous porous media, the mixing of the solute blob is determined by the random sampling of flow and deformation heterogeneity along trajectories, a mechanism different from persistent shear. We derive explicit perturbation theory expressions for stretching-enhanced solute mixing that relate the medium structure and mixing behaviour. The solution is valid for moderate heterogeneity. The random sampling of shear along trajectories leads to a 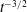 $t^{-3/2}$ decay of the maximum concentration as opposed to an equivalent homogeneous medium, for which it decays as
$t^{-3/2}$ decay of the maximum concentration as opposed to an equivalent homogeneous medium, for which it decays as 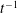 $t^{-1}$.
$t^{-1}$.



