No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
EPA-1088 – The Evaluation of the Effects of Souvenaid on the Quality of Live in Patient with the Diagnosis M.Alzheimer; Real-Life Prospective Clinical Cohort Study
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 April 2020
Abstract
To evaluate the effect of Souvenaid (a multicomponent nutritional drink for early AD) on cognition, behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), activity of daily living (ADL) and well-being of M.Alzheimer patients in a real-life prospective clinical setting.
Patients (and caregivers) with M.Alzheimer, using Souvenaid, were evaluated after 6 months on cognition, behavior, ADL and wellbeing, based on the KATZ Activity of Daily Living, Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Neuro Psychiatric Inventory (NPI).
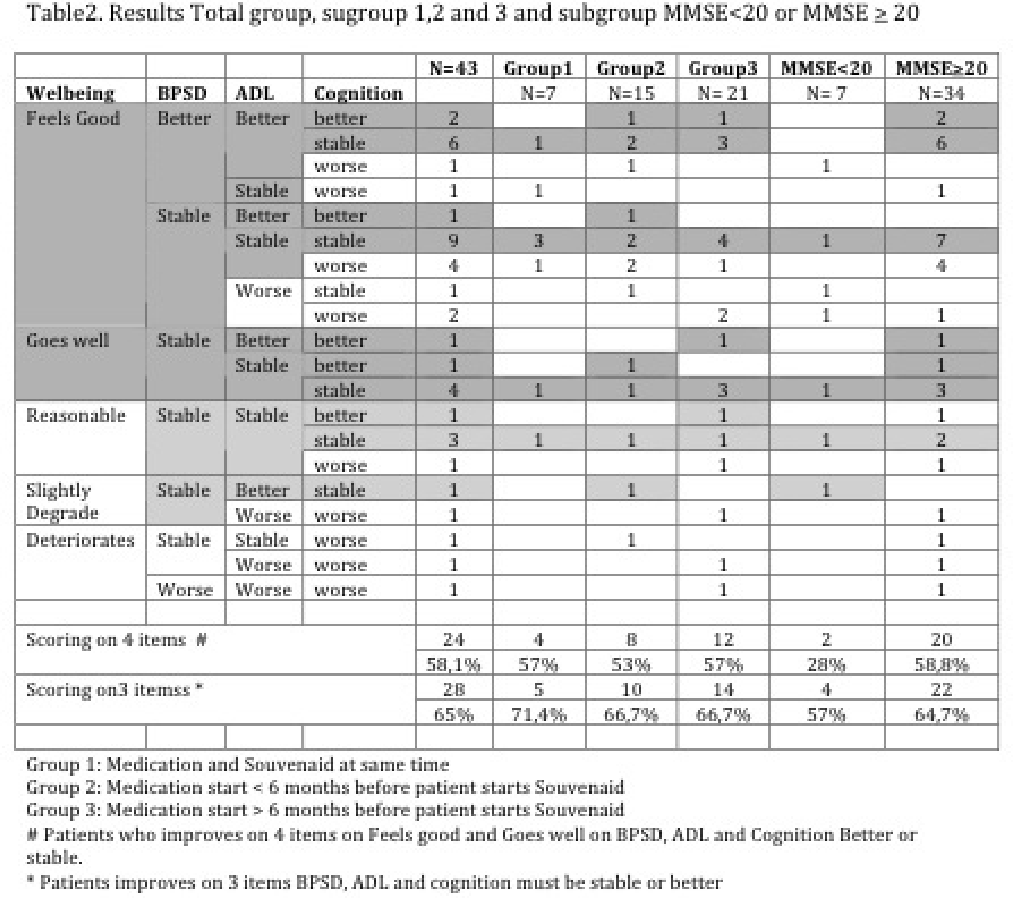
58 Alzheimer patients were included and 43/58 were evaluated after 6-months. 15/58 did not have a follow-up visit yet. 2/58 patients stopped using Souvenaid. 24/43 patients (58,1%) were better or stable on the 4 items mentioned above. 28/43 patients (65%) improved when only evaluating ADL-functions, BPSD and Cognition. Sub-group analyses (1. start Souvenaid and Alzheimer medication together, 2. start Souvenaid < 6 months after start Alzheimer medication, 3. Start Souvenaid > 6 months after start Alzheimer medication); a positive outcome on 4 items was observed in group 1 (57%, 4/7 patients), group 2 (53%, 8/15 patients) and group 3 (57%, 12/21 patients). Another sub-group analyses (MMSE < 20 vs ≥ 20) showed an improvement in 4 items of 28% (2/7 patients) vs 58,8% (20/34 patients).
Souvenaid is well tolerated in a real-life prospective clinical setting, also in conjunction with standard care Alzheimer medication. Souvenaid may be more beneficial in early stage AD patients and seems to improve quality of life.
 |
- Type
- EPW21 – Others 2
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © European Psychiatric Association 2014





Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.