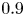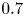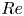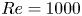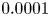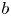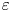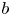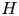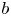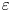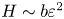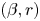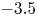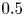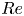95 results
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Study of the Interaction Between Bentonite and a Strain of Bacillus Mucilaginosus
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 538-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
Conditional analysis on extreme wall shear stress and heat flux events in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Instability evolution of a shock-accelerated thin heavy fluid layer in cylindrical geometry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reduced-order variational mode decomposition to reveal transient and non-stationary dynamics in fluid flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 966 / 10 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
11 - The Development of the Contemporary Critical Consciousness Measure-Short
- from Part II - Measurement
-
-
- Book:
- Critical Consciousness
- Published online:
- 20 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 27 April 2023, pp 287-308
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Bubble re-acceleration behaviours in compressible Rayleigh–Taylor instability with isothermal stratification
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2023, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Direct numerical simulation of elastic turbulence in the Taylor–Couette flow: transition pathway and mechanistic insight
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 949 / 25 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2022, A49
-
- Article
- Export citation
Width effect on contact angle hysteresis in a patterned heterogeneous microchannel
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 949 / 25 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blastocyst Stage Affects the Isolation and Culture of Buffalo Naive/Primed Embryonic Stem-Like Cells
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2022, pp. 2093-2104
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wall-cooling effects on pressure fluctuations in compressible turbulent boundary layers from subsonic to hypersonic regimes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Noise reduction mechanisms for insert-type serrations of the NACA-0012 airfoil
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 941 / 25 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2022, A57
-
- Article
- Export citation
2 - Flooding Risk in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin under Global Change
- from Part I - Water-Related Risks under Climate Change
-
-
- Book:
- Climate Risk and Sustainable Water Management
- Published online:
- 17 March 2022
- Print publication:
- 07 April 2022, pp 29-46
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
AlepPBP2, but not AlepPBP3, may involve in the recognition of sex pheromones and maize volatiles in Athetis lepigone
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2022, pp. 536-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
Statistical properties of pressure-Hessian tensor in a turbulent channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 934 / 10 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2022, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of surfactants on the long-wave stability of two-layer oscillatory film flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 928 / 10 December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2021, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
A reverse transition route from inertial to elasticity-dominated turbulence in viscoelastic Taylor–Couette flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 927 / 25 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2021, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Direct numerical simulation of inertio-elastic turbulent Taylor–Couette flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 926 / 10 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2021, A37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Survey of rice production practices and perception of weedy red rice (Oryza sativa f. spontanea) in Taiwan – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 69 / Issue 5 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, p. 615
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification and dynamic expression profiling of circadian clock genes in Spodoptera litura provide new insights into the regulation of sex pheromone communication
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2021, pp. 78-90
-
- Article
- Export citation