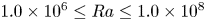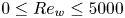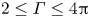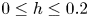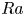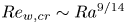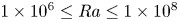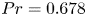53 results
Expression profiling of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) microRNAs and microRNA core genes by Bacillus thuringiensis GS57 infection
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel small-scale self-focusing suppression method for post-compression in high peak power lasers
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antimicrobial peptide cecropin B functions in pathogen resistance of Mythimna separata
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 281-292
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reduced Concentrations of NSE, S100β, Aβ, and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Elderly Patients Receiving Ultrasound-Guided Combined Lumbar Plexus-Sciatic Nerve Block during Hip Replacement
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary chenodeoxycholic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced growth retardation, lipid accumulation and bile acid metabolism disorder in the liver of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 921-934
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fat-free mass may play a dominant role in the association between systolic blood pressure and body composition in children and adolescents
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 622-629
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of monolaurin on intestinal barrier, blood biochemical profile, immunity and antioxidant function in porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus-infected piglets
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2023, pp. 185-192
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotope of the early Permian gabbro and high-Mg diorites from the Zhusileng–Hangwula Belt in the northern Alxa area: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1417-1427
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in breast cancer cells and its effect on reversing tumour drug resistance by alkaloids extracted from traditional Chinese medicine
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 25 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The dysfunction of hormone-sensitive lipase induces lipid deposition and reprogramming of nutrient metabolism in fish
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 588-603
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion management for a 100 PW level laser using a mismatched-grating compressor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AlepPBP2, but not AlepPBP3, may involve in the recognition of sex pheromones and maize volatiles in Athetis lepigone
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2022, pp. 536-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shear-induced modulation on thermal convection over rough plates
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 936 / 10 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2022, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic coupling between carrier and dispersed phases in Rayleigh–Bénard convection laden with inertial isothermal particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 930 / 10 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2021, A24
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, Mediterranean diet and blood lipid profiles in less-developed ethnic minority regions
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2021, pp. 1137-1146
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protocol for a pharmacogenomic study on individualised antipsychotic drug treatment for patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2021, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary selenium sources differentially regulate selenium concentration, mRNA and protein expression of representative selenoproteins in various tissues of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2021, pp. 490-502
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ameliorates high-carbohydrate diet-induced metabolic phenotypes by restoration of intestinal acetate-producing bacteria in Nile Tilapia
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2021, pp. 653-665
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Portable Ultrasonography Onboard Deployment in the PLA(N) Peace Ark Hospital Ship in Mission Harmony 2018
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2021, pp. 835-839
-
- Article
- Export citation