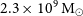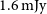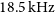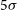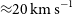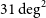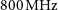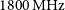120 results
Vapor-Phase Sorption Kinetics for Methanol, Propan-2-OL, and 2-Methylpropan-2-OL on Al3+-, Cr3+-, and Fe3+-Exchanged Montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / October 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 336-342
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy and Electron Diffraction of Mixed-Layer Illite/Smectite: Experimental Results
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / February 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chapter 39 - Termination of Pregnancy at Different Gestational Phases
- from Section 2B - Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare: Termination of Pregnancy
-
-
- Book:
- Textbook of Contraception, Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Published online:
- 16 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 January 2024, pp 239-242
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 36 - Termination of Pregnancy
- from Section 2B - Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare: Termination of Pregnancy
-
-
- Book:
- Textbook of Contraception, Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Published online:
- 16 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 January 2024, pp 223-228
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 37 - Termination of Pregnancy
- from Section 2B - Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare: Termination of Pregnancy
-
-
- Book:
- Textbook of Contraception, Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Published online:
- 16 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 January 2024, pp 229-232
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A Molality-Based BET Equation for Modeling the Activity of Water Sorbed on Clay Minerals
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 6 / December 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 599-609
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contribution of neurological soft signs’ studies to the understanding of the pathophysiology of schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1090
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations Between Depression and Cardiometabolic Health: A 27-Year Longitudinal Study – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 14 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, p. 3018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anhedonia. Depressive versus negative symptom
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S219
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Conducting a pediatric randomized clinical trial during a pandemic: A shift to virtual procedures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2022, e115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Age of the late Holocene Bonneville landslide and submerged forest of the Columbia River Gorge, Oregon and Washington, USA, by radiocarbon dating
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 109 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2022, pp. 65-82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 22 - Management of Unintended Pregnancy
- from Section 4 - Contraception and STIs
-
-
- Book:
- The EBCOG Postgraduate Textbook of Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Published online:
- 24 November 2021
- Print publication:
- 02 December 2021, pp 175-181
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Optimizing chloroacetamide application timing in dicamba-resistant cotton production systems for control of glyphosate-resistant Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 35 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2021, pp. 1007-1013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Delirium in COVID-19: psychopharmacology considerations
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S273-S274
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between depression and cardiometabolic health: A 27-year longitudinal study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 14 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2021, pp. 3007-3017
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey I: Design and first results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2020, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation