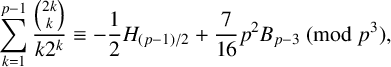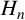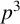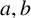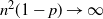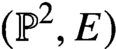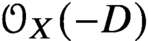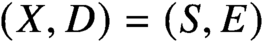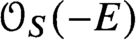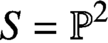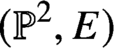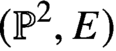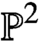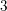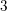18 results
Can ocean heat content regulate Indian summer monsoon rainfall?
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An improved wide-lane ambiguity resolution method for kinematic smartphone positioning
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON SOME CONGRUENCES INVOLVING CENTRAL BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Proof of some conjectural congruences involving Apéry and Apéry-like numbers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, pp. 508-527
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Average Jaccard index of random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
14 - China and Global Health Law in the Face of Covid-19
- from Part V - Human-Centred International Law
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of China and International Law
- Published online:
- 04 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 January 2024, pp 284-301
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Creditor Priority in European Bank Insolvency Law: Financial Stability and the Hierarchy of Claims by Sjur Swensen Ellingsæter [Hart Publishing, London, 2023, 280pp, ISBN: 9781509953653, £85.00 (h/bk)]
-
- Journal:
- International & Comparative Law Quarterly / Volume 72 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, pp. 1091-1094
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On two congruence conjectures of Z.-W. Sun involving Franel numbers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2023, pp. 887-905
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Holomorphic anomaly equation for
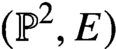 $({\mathbb P}^2,E)$ and the Nekrasov-Shatashvili limit of local
$({\mathbb P}^2,E)$ and the Nekrasov-Shatashvili limit of local  ${\mathbb P}^2$
${\mathbb P}^2$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2021, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
In vivo antimalarial activity and pharmacokinetics of artelinic acid-choline derivative liposomes in rodents
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 147 / Issue 1 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2019, pp. 58-64
-
- Article
- Export citation
The genus-one global mirror theorem for the quintic
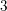 $3$-fold
$3$-fold
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 155 / Issue 5 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2019, pp. 995-1024
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between extrauterine growth restriction and changes of intestinal flora in Chinese preterm infants
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 10 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2019, pp. 513-521
-
- Article
- Export citation
Orbit and Positioning Accuracy for New Generation Beidou Satellites during the Earth Eclipsing Period
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2018, pp. 1069-1087
- Print publication:
- September 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Whole-exome sequencing identifies a Novel SCN5A mutation (C335R) in a Chinese family with arrhythmia
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2018, pp. 688-691
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decades of Chinese Solar and Geophysical Data
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S340 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2018, pp. 71-72
- Print publication:
- February 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Gamma prime stability and its influence on tensile behavior of a wrought superalloy with different Fe contents
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 31 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2016, pp. 1361-1371
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
An SMDP model for a multiclass multi-server queueing control problem considering conversion times
-
- Journal:
- RAIRO - Operations Research / Volume 48 / Issue 4 / October 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2014, pp. 615-639
- Print publication:
- October 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation