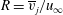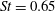92 results
Reducing treatment delays of first episode psychosis through policy in Canada: a mixed methods analysis of service provider perspectives
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S386-S387
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Radiation and Chemical Program Research for Multi-Utility and Repurposed Countermeasures: A US Department of Health and Human Services Agencies Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2024, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (Neupogen®; Filgrastim) Accelerates Neutrophil Recovery in a Rodent Model of Sulfur Mustard-Induced Hematologic Toxicity
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e550
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 41 - Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
- from Section 7 - Hepato-Renal and Gastrointestinal Conditions in Pregnancy
-
-
- Book:
- OSCEs in Obstetrics and Maternal-Fetal Medicine
- Published online:
- 23 February 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 February 2023, pp 531-541
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Feasibility of telemedicine research visits in people with Parkinson’s disease residing in medically underserved areas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, e133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unusual combination of three types of interatrial communications in a child
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2020, pp. 1933-1934
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of small-volume gastrografin videofluoroscopic screening for detecting pharyngeal leaks following total laryngectomy
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 4 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2020, pp. 350-353
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Feasibility of ovine and synthetic temporal bone models for simulation training in endoscopic ear surgery
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 133 / Issue 11 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2019, pp. 966-973
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Do we know how scabies outbreaks in residential and nursing care homes for the elderly should be managed? A systematic review of interventions using a novel approach to assess evidence quality
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 147 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, e250
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identifying eigenmodes of averaged small-amplitude perturbations to turbulent channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 875 / 25 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2019, pp. 758-780
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Artificial intelligence/machine learning in manufacturing and inspection: A GE perspective
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 7 / July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2019, pp. 545-558
- Print publication:
- July 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Peri-operative outcomes following major surgery for head and neck cancer in the elderly: institutional audit and case–control study
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 132 / Issue 8 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2018, pp. 742-747
- Print publication:
- August 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nickel-reduced graphene oxide composite foams for electrochemical oxidation processes: towards biomolecule sensing
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 8 / Issue 3 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2018, pp. 695-702
- Print publication:
- September 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Management of late presentation congenital heart disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 27 / Issue S6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2017, pp. S31-S39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The management of scabies outbreaks in residential care facilities for the elderly in England: a review of current health protection guidelines
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 144 / Issue 15 / November 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2016, pp. 3121-3130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Damping of modal perturbations in solid rocket motors
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 120 / Issue 1231 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2016, pp. 1425-1445
-
- Article
- Export citation
Twin pregnancy in a Fontan-palliated patient
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2016, pp. 1221-1224
-
- Article
- Export citation
Descending aortic flow reversal in obstructed total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 26 / Issue 5 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2016, pp. 1002-1004
-
- Article
- Export citation
A numerical study of shear layer characteristics of low-speed transverse jets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 790 / 10 March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2016, pp. 275-307
-
- Article
- Export citation