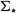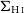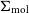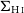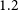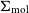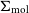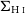73 results
VERTICO V: The environmentally driven evolution of the inner cold gas discs of Virgo cluster galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, e017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Memphis Pandemic Health Informatics System (MEMPHI-SYS)—Creating a Metropolitan COVID-19 Data Registry Linked Directly to Community Testing to Enhance Population Health Surveillance
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, e326
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Use of Portable Oxygen Concentrators in Low-Resource Settings: A Systematic Review
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2022, pp. 247-254
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
The long-term sustainability of a respiratory culture nudge
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2022, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Growth from birth to 6 months of infants with and without intrauterine preeclampsia exposure
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2021, pp. 151-155
-
- Article
- Export citation
34 Long-Term Deutetrabenazine Treatment Response in Tardive Dyskinesia by Concomitant Dopamine-Receptor Antagonists and Baseline Comorbidities
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2019, p. 193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
45 Long-term Treatment with Deutetrabenazine Is Associated with Continued Improvement in Tardive Dyskinesia: Results from an Open-label Extension Study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2019, pp. 200-201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
46 Confirmed Safety of Deutetrabenazine for Tardive Dyskinesia in a 2-Year Open-label Extension Study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2019, p. 201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
35 Long-term Improvements in Site-Rated Outcomes with Deutetrabenazine Treatment in Patients with Tardive Dyskinesia
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2019, pp. 193-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
158 Long-Term Safety of Deutetrabenazine for the Treatment of Tardive Dyskinesia: Results From an Open-Label, Long-Term Study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2018, p. 97
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
149 Deutetrabenazine for the Treatment of Tardive Dyskinesia: Results From an Open-Label, Long-Term Study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2018, pp. 92-93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
134 Improvements in Clinical Global Impression of Change With Deutetrabenazine Treatment in Tardive Dyskinesia From the ARM-TD and AIM-TD Studies
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2018, p. 84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Neotoma Paleoecology Database, a multiproxy, international, community-curated data resource
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / January 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2018, pp. 156-177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prehospital Modified HEART Score Predictive of 30-Day Adverse Cardiac Events
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2018, pp. 58-62
- Print publication:
- February 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Quantity of Melt Water in the Marble Point–Gneiss Point Area McMurdo Sound, Antarctica*
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 7 / Issue 50 / 1968
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2017, pp. 313-320
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Palynological Evidence for Early Holocene Aridity in the Southern Sierra Nevada, California
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / November 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 322-332
-
- Article
- Export citation
Oat (Avena sativa) Response to Imazapic Residues
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / December 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 875-878
-
- Article
- Export citation
Agricultural Weed Research: A Critique and Two Proposals
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 62 / Issue 4 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 672-678
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cotton Stage of Growth Determines Sensitivity to 2,4-D
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 601-610
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infections Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 37 / Issue 7 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2016, pp. 827-833
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation