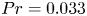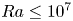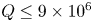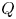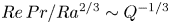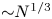472 results
Obsessive-compulsive disorder and suicide: a longitudinal study in Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EXPERIMENTAL CONDITIONS FOR 14C GRAPHITE PREPARATION AT THE GXNU LAB, CHINA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SAMPLE PREPARATION SYSTEM FOR CARBONATE AND DIC IN WATER AT THE GXNU-AMS LABORATORY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparative epidemiology of bacteraemia in two ageing populations: Singapore and Denmark
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
98 The Crosstalk between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Preterm Infants with Pain/Stress in the NICU
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Mineralogy of Dickite and Nacrite From Northern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 49 / Issue 6 / December 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 586-595
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Kaolin Mineralogy of Clays in Paleosol Profiles on the Late-Miocene Sediments in Penghu Islands (Pescadores), Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / February 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Vision-based food handling system for high-resemblance random food items
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
P199: Cluster analysis dissecting cognitive deficits in older adults with major depressive disorder and the association between neurofilament light chain
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 188-189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of horizontal magnetic fields on turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cuboid vessel with aspect ratio Γ = 5
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kaolin Minerals from Chinmen Island (Quemoy)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 130-137
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Direct Synthesis of 5A Zeolite From Palygorskite: The Influence of Crystallization Directing Agent on the Separation Performance for Hexane Isomers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Novel KDM2B/SAV1 Signaling Pathway Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Origin and Mineralogy of Sepiolite and Palygorskite From the Tuluanshan Formation, Eastern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 521-530
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Upregulated Solute Carrier SLC39A1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Proliferation and Indicates Unfavorable Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Structural Controls on the Catalytic Polymerization of Hydroquinone by Birnessites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 525-537
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Charge State of Protons with 90 and 100 keV Energies Decelerated in Hydrogen Plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modernity and Confucian Political Philosophy in a Globalizing World
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PP70 Mapping Of Health Technology Assessment In China: A Comparative Study Between 2016 And 2021
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation