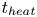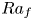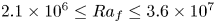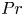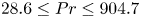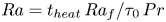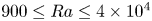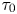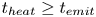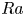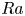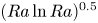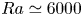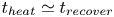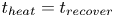195 results

Australian Banking and Finance Law and Regulation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- December 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Investigations on ancient bronze drums from Majiang, Guangxi, P. R. China
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variation in the structural order of kaolinite in regolith as an effective indicator of REE mineralization
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Formation and evolution of laminar thermal structures: correlation to the thermal boundary layer and effects of heating time
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, A60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Density functional theory study of the atomic and electronic structures of trans-vacant 1M Al-rich illite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2024, pp. 388-394
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chinese stalagmite δ18O records reveal the diverse moisture trajectories during the middle to late last glacial period
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distribution and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Ion Adsorption-type REE Deposit (IAD) at Maofeng Mountain, Guangzhou, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 340-361
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Composition and Growth Mechanism of Coexisting 4M2 and 4A8 Biotite Polytypes from Rhyolite of Long Valley Caldera, California
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 48-61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intelligent Optimization of Parameters for Tens of MA-Class Z-Pinch Accelerators
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Metastasis of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma through Targeting Carcinogenic miR-301b-3p
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mineralogical Evolution of the Paleogene Formations in the Kyzyltokoy Basin, Kyrgyzstan: Implications for the Formation of Glauconite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 43-60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Correlation between Photoluminescence Properties of Surface Defects and Laser-Induced Damage Threshold of Fused Silica
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Digital generation of super-Gaussian perfect vortex beams via wavefront shaping with globally adaptive feedback
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
China On the Legislative Concept and the New Rules of the Succession System of the Civil Code in China
-
-
- Book:
- International Survey of Family Law 2023
- Published by:
- Intersentia
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 October 2023, pp 225-258
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Local structural and functional MRI markers of compulsive behaviors and obsessive–compulsive disorder diagnosis within striatum-based circuits
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 710-720
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social mixing and network characteristics of COVID-19 patients before and after widespread interventions: A population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of novel functional brain proteins for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: Based on a proteome-wide association study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diet supplementation of organic zinc positively affects growth, antioxidant capacity, immune response and lipid metabolism in juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, pp. 1689-1703
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Human–animal–environment dynamics and formation of pastoralism in the southern Tibetan Plateau during the Middle–Late Holocene
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 114 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, pp. 30-51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation