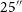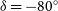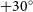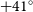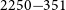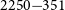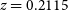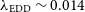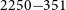148 results
L-Shell X-Ray Conversion Yields for Laser-Irradiated Tin and Silver Foils
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reductive Degradation of p,p′-DDT cy Fe(II) in Nontronite NAu-2
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 6 / December 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 821-836
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation in the clinical management of self-harm by area-level socio-economic deprivation: findings from the multicenter study of self-harm in England
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 1004-1015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydra II: Characterisation of Aegean, Caesar, ProFound, PyBDSF, and Selavy source finders
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydra I: An extensible multi-source-finder comparison and cataloguing tool
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e028
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The usability of daytime and night-time heart rate dynamics as digital biomarkers of depression severity
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 8 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 3249-3260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between persistent cognitive difficulties and depression and functional outcomes in people with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2022, pp. 6334-6344
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Remote Assessment of Disease and Relapse in Major Depressive Disorder (RADAR-MDD): Recruitment, retention, and data availability in a longitudinal remote measurement study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Long-term effectiveness of Self-Help Plus in refugees and asylum seekers resettled in Western Europe: 12-month outcomes of a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2022, e39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey Paper II: First Stokes I Source Catalogue Data Release
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2021, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Home enteral feed dietitians save unnecessary hospital admissions of patients with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 67 / Issue OCE3 / May 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2021, E108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A history of high-power laser research and development in the United Kingdom
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unexpected circular radio objects at high Galactic latitude
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2021, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey I: Design and first results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2020, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Managing uncertainty: Principles for improved decision making
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 25 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2020, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P-863 - the Safety of Specialty Trainees in Psychiatry
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PKS 2250–351: A giant radio galaxy in Abell 3936
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2020, e013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation