Article contents
Design and performances of a shielded liquid helium insert with an optically heated variable temperature stage for the study of low frequency magnetic noise in HTc superconductors*
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 March 2001
Abstract
We have designed and built a liquid helium immersion insert which is magnetically shielded from the ambient magnetic field fluctuations by the use of a superconducting lead can. The insert has a variable temperature stage made of sapphire which is optically heated by the light guided from an external lamp via a glass rod. The temperature regulation is achieved by the use of a commercial PID controller: the temperature of the sapphire ranges from 50 K to 100 K with peak to peak fluctuations less than 20 mK over a 3 minutes observation period. The magnetic noise inside the insert has been measured with a low Tc dc-SQUID and the white noise level above 200 Hz is less than 4 fT/$\sqrt{\rm Hz}$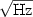 . Furthermore, the magnetic attenuation factor due to the superconducting lead can is greater than 26 500 for frequencies above 15 Hz. This cryogenic insert is used for studying low frequency vortex noise in high Tc superconducting thin films at different temperatures and the field penetration in the films as a function of the applied magnetic field during its transition state.
. Furthermore, the magnetic attenuation factor due to the superconducting lead can is greater than 26 500 for frequencies above 15 Hz. This cryogenic insert is used for studying low frequency vortex noise in high Tc superconducting thin films at different temperatures and the field penetration in the films as a function of the applied magnetic field during its transition state.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2001
Footnotes
This paper has been presented at “Sixièmes journées de cryogénie et supraconductivité”, 16 May 2000, Aussois.
References
- 1
- Cited by




