Capturing meal images using mobile phone cameras is a promising alternative to traditional dietary assessment methods. Acquiring photos is reasonably simple but nutritional content analysis of images is a major challenge. Automated food identification and portion size assessment is computationally and participant intensive; relying on participant feedback for accuracy(Reference Boushey, Kerr and Schap1). Dietitian analysis of photos is accurate but time-consuming and expensive(Reference Martin, Correa and Han2). Crowdsourcing could offer a rapid low-cost alternative by utilising the life-long experience that all humans have in food identification. Previous crowdsourcing methods include the Eatery app, which produces a simple 11-point ‘healthiness’ scale for each meal(Reference Turner-McGrievy, Helander and Kaipainen3) and the PlateMate system, which creates a list of all individual foods with portion sizes, energy and macronutrient content(Reference Noronha, Hysen and Zhang4). While the Eatery produces limited and subjective data on meal content, PlateMate represents a complex integrated system of multiple tasks requiring on average 25 workers, costing £2·75 and taking 90 min per image. For feasible data-capture in a large-scale longitudinal studies, crowdsourcing data from meal photos needs to be cheaper and quicker. We aimed to develop a simpler task and tested it's feasibility for crowdsourcing dietary data.
FoodFinder, a single task for identifying food groups and portion sizes, developed using Qualtrics (www.qualtrics.com/), and linked to the Prolific Academic (https://prolific.ac/) crowdsourcing platform for recruitment and reimbursement of a UK crowd. Thirty meal photos with measured total meal weight (grams) were analysed by a dietitian and crowds ranging in size from 5 to 50 people. The difference between actual meal weight (the gold-standard) and total meal weight estimated by different sized crowds and ratings by a dietician were compared to each other. To establish group consensus crowd estimates were weighted by majority agreement(Reference Zhai, Hachen and Kijewski-Correa5). Bland-Altman analysis assessed agreement with actual meal weight.
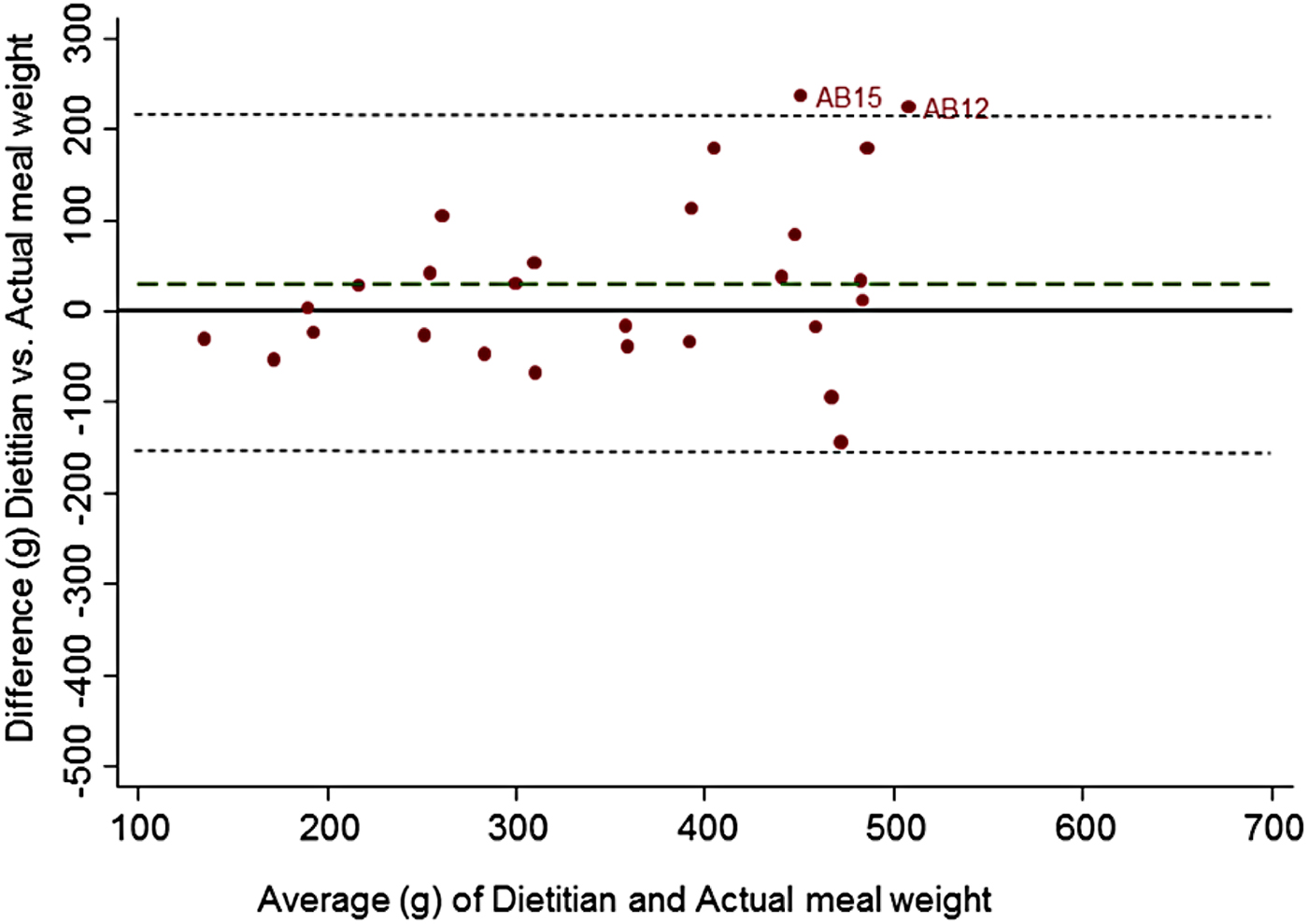
Fig. 1
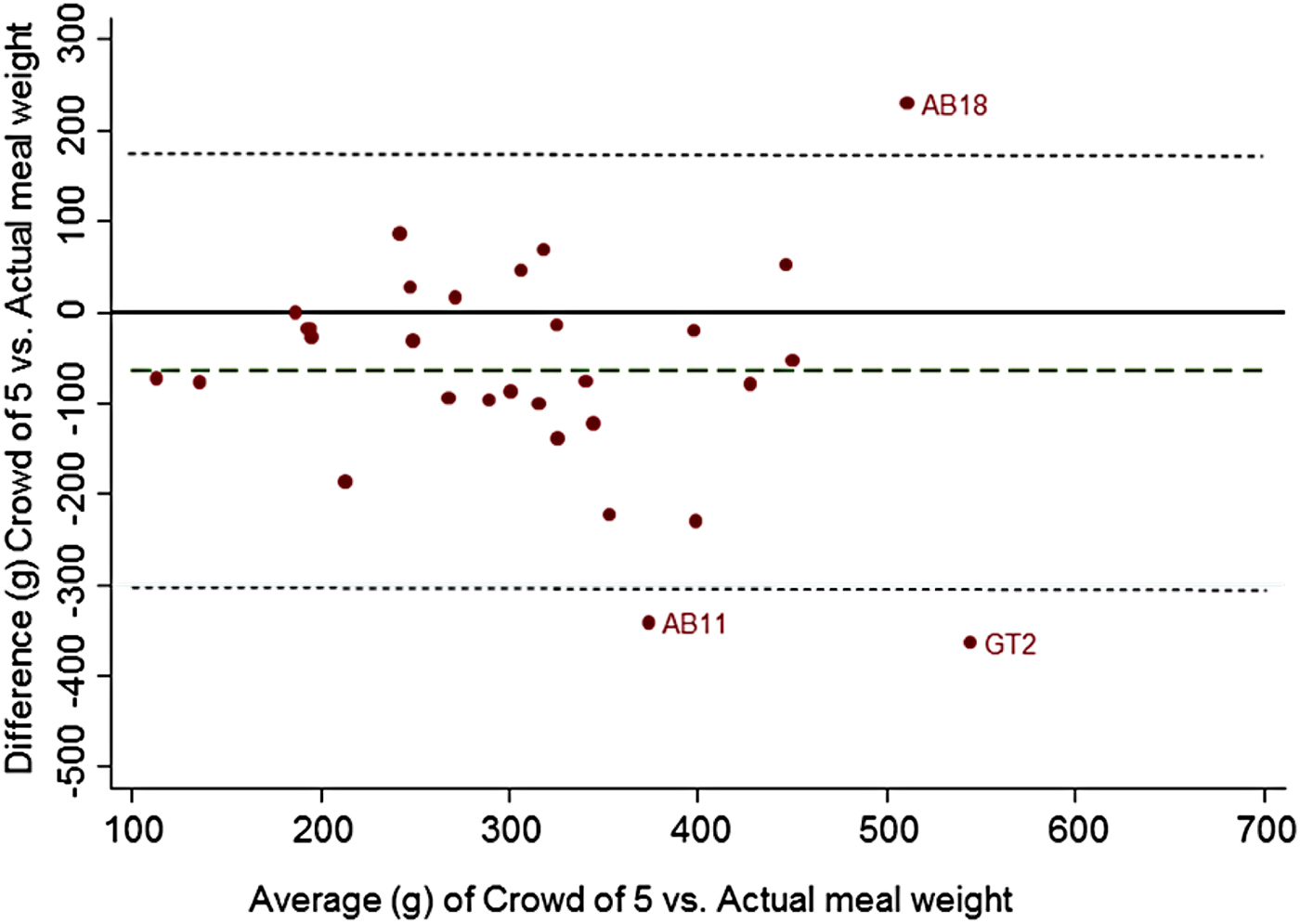
Fig. 2
A crowd of 5 people underestimated true meal weight by 63 g, equating to 15 % of actual meal weight with limits of agreement (LOA) from −299 to 174 g. In comparison experts overestimated by 28 g equating to 9 % of actual meal weight with LOA −158, 214 g. With a crowd of 5 people, crowdsourcing cost £3·35 and took a mean 2 mins 55 sec (SD 2 min 6 sec) per image. A crowd of 50 had similar accuracy and limits of agreement (−65 g LOA −278, 149 g) but was more expensive. Further development of FoodFinder is required to make rapid low-cost analysis of meal photos via crowdsourcing a feasible method for assessing diet.
This work was supported by a catalyst award from the Elizabeth Blackwell Institute for Health Research, which is co-funded by the University of Bristol and an Institutional Strategic Support Fund from the Wellcome Trust.




