Article contents
Yttria-stabilized barium zirconate surface reactivity at elevated temperatures
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 June 2020
Abstract
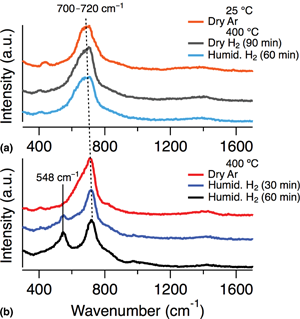
Material changes in yttrium-doped barium zirconate, BaZr0.8Y0.2O3–x, were studied using in situ Raman spectroscopy and ex situ x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. During in situ Raman analysis, samples were heated to temperatures of 300–600 °C and exposed to both dry and humidified H2 atmospheres. At the lower temperatures (300–450 °C), a new vibrational peak appears in the Raman spectra during exposure to humidified H2. The appearance of this feature is reversible, dependent on previous sample history, and possibly results from new, secondary phase formation or lattice distortion.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society, 2020
References
- 1
- Cited by





