Article contents
Self-ion irradiation effects on mechanical properties of nanocrystalline zirconium films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 July 2017
Abstract
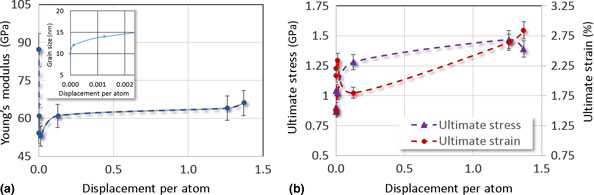
Zirconium thin films were irradiated at room temperature with an 800 keV Zr+ beam using a 6 MV HVE Tandem accelerator to 1.36 displacement per atom damage. Freestanding tensile specimens, 100 nm thick and 10 nm grain size, were tested in situ inside a transmission electron microscope. Significant grain growth (>300%), texture evolution, and displacement damage defects were observed. Stress–strain profiles were mostly linear elastic below 20 nm grain size, but above this limit, the samples demonstrated yielding and strain hardening. Experimental results support the hypothesis that grain boundaries in nanocrystalline metals act as very effective defect sinks.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
References
- 4
- Cited by




